AI ethics is the field that examines how to develop and use artificial intelligence systems in ways that align with human values like fairness, safety, and respect for rights.
As AI systems make more decisions that affect people’s lives — from hiring employees to diagnosing medical conditions — the need for ethical guidelines has become urgent. These systems can perpetuate biases, invade privacy, or cause harm if not designed with careful oversight. Companies, governments, and researchers now recognize that building AI without ethical consideration creates serious risks.
The consequences of unethical AI have already appeared in real-world situations. Facial recognition systems have shown higher error rates for people with darker skin tones. Hiring algorithms have discriminated against women and minorities. Credit scoring systems have denied loans based on biased data patterns.
AI ethics provides frameworks to prevent these problems before they occur. The field brings together computer scientists, philosophers, lawyers, and policymakers to establish standards for responsible AI development. Organizations worldwide are now implementing ethical guidelines to ensure AI systems serve society’s best interests while minimizing potential harms.
What Is AI Ethics
AI ethics connects artificial intelligence technology with moral principles that guide right and wrong behavior. The field emerged as AI systems gained the ability to make decisions that traditionally required human judgment. Unlike simple computer programs that follow fixed rules, AI systems learn patterns from data and make predictions that can affect real people’s lives.
The discipline draws from multiple fields including computer science, philosophy, law, and social science. Each area contributes essential perspectives on how intelligent systems interact with human society. Computer scientists provide technical knowledge about how AI works, while philosophers contribute frameworks for ethical reasoning.

Source: ResearchGate
AI ethics addresses both immediate practical concerns and broader questions about technology’s role in society. Immediate concerns include preventing discrimination in hiring algorithms or ensuring medical AI systems work equally well for all patients. Broader questions involve how much decision-making authority AI systems have and how to preserve human agency in an automated world.
Why Organizations Need AI Ethics
Organizations implementing AI systems face mounting pressure to address ethical considerations as these technologies become integral to business operations. Financial institutions using biased lending algorithms risk violating fair lending laws and facing regulatory action. Healthcare organizations deploying AI diagnostic tools face potential medical errors if these systems don’t work accurately across different patient populations.
The EU AI Act represents the first comprehensive AI regulation, establishing risk-based requirements for AI systems operating in European markets. Organizations deploying AI systems classified as high-risk face fines up to seven percent of global annual revenue for non-compliance.
High-profile AI failures demonstrate the costs of inadequate ethical oversight:
- Microsoft’s Tay chatbot learned offensive behavior from social media interactions, forcing the company to shut down the system within 24 hours
- Amazon discontinued an AI recruiting tool after discovering it systematically discriminated against women candidates
- Healthcare AI systems have shown performance disparities across racial groups, leading to patient safety concerns
Organizations with strong AI ethics programs can prevent costly incidents through proactive risk assessment, bias testing, and stakeholder engagement. Small businesses implementing AI solutions benefit from establishing ethical frameworks early in their AI adoption journey.
Core Principles of AI Ethics
Seven fundamental principles form the foundation of most AI ethics frameworks worldwide. These principles address essential questions about AI development and deployment across different cultures and organizations.
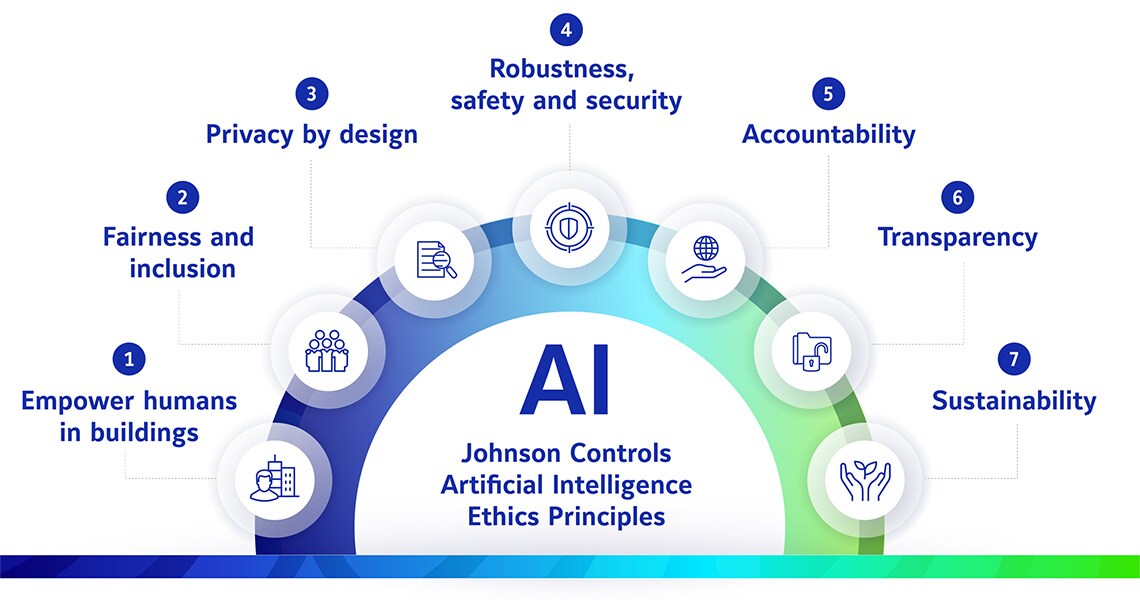
Source: Johnson Controls
- Transparency and Explainability requires that AI systems provide clear explanations for their decisions, especially in high-stakes applications. Users and affected individuals can understand how AI systems work and why specific decisions were made. This principle enables accountability and allows people to challenge unfair or incorrect automated decisions.
- Fairness and Non-Discrimination demands that AI systems avoid discrimination and treat all individuals equitably. Organizations actively test for and mitigate different types of bias that can emerge in AI systems. This includes bias from training data, algorithmic design choices, and deployment practices that might disadvantage certain groups.
- Accountability establishes clear responsibility for AI system outcomes. Organizations designate specific individuals or teams responsible for AI decisions and their consequences. Clear accountability structures enable appropriate oversight and ensure someone can address problems when they arise.
- Privacy Protection requires safeguarding personal information used to train and operate AI systems. Organizations obtain appropriate consent for data use, implement security measures to protect sensitive information, and provide individuals with control over their personal data.
- Human Oversight ensures that humans maintain meaningful control over AI systems, particularly for decisions with significant consequences. This principle recognizes that AI augments rather than replaces human judgment in important areas like healthcare, criminal justice, and employment.
- Safety and Security requires AI systems to operate reliably without causing harm and include protections against malicious attacks or misuse. This encompasses both direct physical risks from AI systems and more subtle psychological or social harms.
- Beneficence and Autonomy ensures AI systems promote positive outcomes while actively preventing harm and respecting human choice and decision-making authority.
Common AI Ethics Challenges
Algorithmic bias represents one of the most pervasive challenges in AI ethics. Bias can emerge from multiple sources including training data that reflects historical discrimination, algorithms designed without considering fairness, and deployment practices that affect different groups unequally.
Privacy protection creates complex technical and legal challenges as AI systems typically require large amounts of personal data to function effectively. Organizations balance the need for comprehensive datasets with privacy protection requirements from regulations like GDPR. The challenge intensifies when effective bias detection requires access to sensitive demographic information about individuals.
Transparency conflicts with other important objectives like privacy protection and competitive advantage. Many AI systems function as “black boxes” where the decision-making process is difficult to understand or explain. Deep learning models can involve millions of parameters that interact in complex ways, making it challenging to provide simple explanations for their decisions.
Security vulnerabilities expose AI systems to various attacks that can compromise both system integrity and user privacy:
- Adversarial attacks — fool AI systems into making incorrect decisions by subtly modifying input data
- Data poisoning attacks — corrupt training datasets to manipulate AI system behavior
- Model extraction attacks — attempt to steal proprietary AI models or sensitive information
Global coordination proves difficult as different regions prioritize ethical considerations differently and maintain varying regulatory approaches.
How to Implement AI Ethics in Your Organization
Successful AI ethics implementation begins with establishing governance frameworks that unite stakeholders across technology, legal, risk management, and business teams. Organizations define specific governing principles that align with both standard ethical principles and unique organizational values.
The NIST framework provides four core functions for trustworthy AI systems. The mapping function outlines the purpose, goals, and expectations of AI systems. The measurement function evaluates performance against objectives and introduces controls. The management function provides mechanisms for optimization when risks arise. The governance function involves continuous monitoring through oversight mechanisms.
Key implementation controls include attribution capabilities that identify sources of AI-generated content, security measures that protect against unauthorized access, and consent mechanisms that obtain permission before collecting personal information.
Create Ethics Review Processes

Source: ResearchGate
Ethics review processes create systematic checkpoints throughout AI project lifecycles to identify and address ethical concerns before deployment. Organizations design these processes to evaluate AI systems at critical decision points: project initiation, data collection, model development, testing, and deployment.
Review committees examine each AI project against established ethical criteria. Common evaluation areas include data representativeness, algorithm transparency, bias detection results, privacy protection measures, and potential societal impacts. Projects receive approval, conditional approval with required modifications, or rejection based on ethics assessments.
Generative AI development requires particular attention to content attribution, potential misuse, and training data provenance during the review process.
Train Teams on Ethical AI Practices
Comprehensive training programs build AI ethics capabilities across organizational levels and functions. Technical teams receive specialized training on bias detection techniques, fairness metrics, and algorithmic transparency methods. Business stakeholders participate in training that covers AI capabilities, limitations, and ethical implications for their specific domains.
Training programs include hands-on exercises using real-world case studies and scenarios relevant to the organization’s industry and use cases. Marketing teams implementing AI systems benefit from targeted training on customer consent, personalization ethics, and transparent advertising practices.
Building Ethical AI for Long-Term Success
Organizations that implement ethical AI practices create sustainable competitive advantages that extend beyond regulatory compliance. Ethical AI development reduces legal risks, builds customer trust, and attracts top talent who want to work on responsible technology projects.
Human-centered AI approaches prioritize human needs and values throughout AI system development and deployment. Organizations that embed human centricity in AI processes create more responsible and effective systems that complement rather than replace human intelligence and creativity.
Ethical impact assessments provide structured evaluation of potential implications before AI system deployment. These assessments consider various stakeholder perspectives, potential risks and benefits, and alternative approaches that might better serve ethical objectives. Interdisciplinary teams including ethicists, domain experts, and community representatives conduct these evaluations.
Ethics committees bring together representatives from technology, legal, risk management, and leadership teams to provide rigorous oversight of AI development and deployment. These committees define review processes for new AI developments, create training programs, and provide ongoing guidance on ethical issues that arise during implementation.
Retail organizations using AI for customer recommendations and inventory management can implement ethical frameworks that respect customer privacy while delivering personalized experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Ethics
How can organizations evaluate vendors for ethical AI practices?
Look for transparency in algorithms, bias testing protocols, and clear accountability measures. Effective vendors provide detailed documentation explaining how their AI systems make decisions and what data influences those decisions. They conduct regular bias testing across different demographic groups and publish results from these assessments.
Strong vendors maintain ethics committees that review AI development, offer clear policies for handling algorithmic errors, and provide audit trails showing how they address fairness concerns. They also demonstrate compliance with regulations like GDPR and offer ongoing monitoring services.
AI chatbot development providers should demonstrate ethical conversation design, bias mitigation in responses, and clear data handling practices.
What fairness metrics work best for measuring AI bias?

Source: Superwise
Common fairness metrics include demographic parity, equalized odds, and individual fairness measures. Demographic parity ensures that positive outcomes occur at equal rates across different groups. Equalized odds focuses on ensuring that error rates remain consistent across groups. Individual fairness measures ensure that similar people receive similar treatment regardless of group membership.
Choose metrics aligned with your specific use case and stakeholder values. Credit scoring systems might prioritize demographic parity to ensure equal access to financial services, while medical diagnostic tools might focus on equalized odds to maintain consistent accuracy across patient populations.
How long does establishing AI governance typically take?
Basic frameworks can be established in three to four months, while comprehensive governance systems typically require six to twelve months. Organizations with existing risk management processes can often adapt their structures to include AI governance within the shorter timeframe.
Comprehensive governance systems include detailed bias testing protocols, ethics review committees, stakeholder engagement processes, and integrated monitoring platforms. Organizations starting without existing governance structures may need additional time to build foundational policies and train staff.
The Path Forward for Ethical AI
The evolution of AI ethics from philosophical consideration to practical necessity reflects the urgent need for responsible approaches to artificial intelligence. Organizations implementing ethical AI frameworks position themselves for sustainable success by building stakeholder trust, reducing regulatory risks, and creating more robust AI systems.
Success in building ethical AI depends on recognizing that technology alone cannot solve ethical challenges. The future requires sustained collaboration between technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and affected communities to ensure that artificial intelligence serves human flourishing rather than narrow organizational interests.
The implementation of robust ethical frameworks represents both a moral imperative and a strategic necessity for any organization seeking to build sustainable value through AI technologies. As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly central to business operations and daily life, organizations that proactively address ethical considerations will be best positioned to harness AI’s potential while protecting fundamental human values.


