Artificial intelligence in insurance refers to computer systems that analyze data, make predictions, and automate tasks traditionally performed by human insurance professionals.
The insurance industry is experiencing a digital transformation driven by artificial intelligence technologies. Traditional insurance operations relied heavily on manual processes, paper-based documentation, and human judgment for critical decisions like underwriting and claims processing. These manual approaches often required weeks or months to complete routine transactions.
Modern AI systems can process vast amounts of data in minutes rather than days. Insurance companies now use machine learning algorithms to assess risk, natural language processing to analyze documents, and computer vision to evaluate property damage from photographs. These technologies enable faster decision-making while maintaining accuracy standards.
How AI Transforms Insurance Operations
AI applications in insurance span multiple business functions, from customer service to fraud detection. These systems handle routine tasks automatically while flagging complex cases for human review.

Source: Multimodal
Document processing represents one of the most common AI applications in insurance. AI platforms can process market reform contracts and loss runs from brokers without human intervention. The technology classifies documents and routes them to appropriate departments based on content analysis.
Natural language processing enables AI systems to read and interpret complex insurance documents. Computer vision algorithms analyze photographs of damaged property to assess repair costs and identify fraud indicators. These capabilities allow insurers to make preliminary decisions on many claims without human review.
Risk Assessment and Underwriting Automation
AI transforms how insurance companies evaluate and price risk by analyzing multiple data sources simultaneously. Traditional risk assessment relied primarily on historical claims data and basic demographic information. Modern AI systems incorporate real-time data from satellites, weather services, and Internet of Things devices.

Source: FinTech Global
Machine learning algorithms identify patterns in customer behavior, property characteristics, and environmental factors that indicate potential risks. For example, AI systems can analyze satellite imagery to detect structural issues in buildings or measure property dimensions for accurate valuation.
Predictive models help insurers anticipate future claims and adjust coverage accordingly. A homeowner moving to a hurricane-prone area might receive automatic recommendations for flood insurance based on AI analysis of geographic risk factors.
Claims Processing Enhancement
AI significantly accelerates claims processing while improving accuracy and fraud detection capabilities. Traditional claims processing required manual review of documentation, phone calls with customers, and physical inspections that could take weeks to complete.

Source: Debut Infotech
Natural language processing analyzes claim descriptions and supporting documents to assess validity automatically. Computer vision examines photographs of damage to estimate repair costs and identify inconsistencies that might indicate fraud.
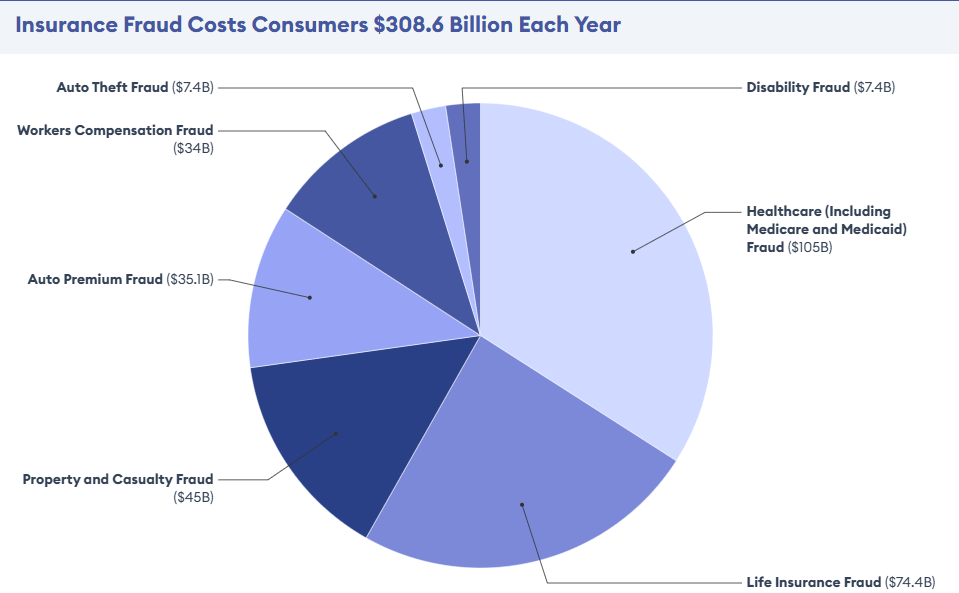
Machine learning algorithms compare new claims against historical fraud patterns to flag suspicious cases. The Coalition Against Insurance Fraud estimates that insurance fraud costs $308 billion annually in the United States.
Customer Service Applications
AI-powered customer service systems provide 24/7 support through chatbots and virtual assistants that handle common inquiries about policy details, coverage explanations, and billing information. These systems understand natural language and maintain conversation context to provide helpful responses.
Modern AI chatbots go beyond simple question-and-answer interactions to provide personalized recommendations based on customer profiles and transaction histories. The systems can suggest policy modifications, coverage additions, or discounts that align with individual customer needs.
Customer onboarding processes benefit from AI automation that guides new policyholders through applications and explains policy terms. AI systems verify documentation and provide coverage recommendations based on individual risk assessments.
Personalized Insurance Experiences
AI systems analyze customer data to identify coverage gaps and suggest appropriate policy adjustments or additional coverage options. The technology examines factors such as life changes, geographic location, asset values, and risk profiles to generate personalized recommendations.
Machine learning algorithms process historical claims data, customer behavior patterns, and demographic information to predict insurance needs. The systems can recommend specific coverage amounts, policy riders, or entirely new insurance products based on individual customer circumstances.
Cross-selling opportunities emerge naturally from AI analysis of customer data and life events. The technology can identify when customers might benefit from additional insurance products, such as recommending homeowner’s insurance when someone purchases auto insurance.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI fraud detection systems use advanced pattern recognition and machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious insurance claims before fraudulent payments occur. These systems analyze millions of claims in real-time, comparing each submission against historical fraud patterns and behavioral indicators.
Pattern recognition forms the foundation of AI fraud detection. Machine learning models examine historical claims data to identify subtle correlations and indicators that human investigators might miss.
Anomaly detection algorithms continuously monitor claim submissions for unusual patterns or behaviors that deviate from normal claim characteristics. These systems can detect inconsistencies in claim narratives, identify unusual billing patterns, and recognize fraudulent documentation.
Common Fraud Indicators
AI systems detect various fraud indicators that help investigators prioritize their efforts:
- Timing anomalies — Claims submitted immediately after policy inception or just before policy expiration
- Geographic clustering — Multiple similar claims from the same location or provider within short timeframes
- Documentation inconsistencies — Discrepancies between police reports, medical records, and claim descriptions
- Billing pattern irregularities — Unusual charges, duplicate billing, or inflated repair estimates
- Provider red flags — Claims involving medical providers or repair shops with previous fraud convictions
Natural language processing technology analyzes claim descriptions and supporting documentation to identify suspicious language patterns or contradictory statements. These systems can detect when claim narratives contain inconsistencies or when the described incident doesn’t align with typical accident scenarios.
Benefits of AI Implementation
Insurance companies gain significant advantages when implementing artificial intelligence across their operations. AI transforms traditional insurance processes by automating routine tasks, enhancing decision-making capabilities, and improving customer interactions.

Source: Creatio
Operational Efficiency Improvements
AI dramatically reduces the time required to complete routine insurance tasks. Document processing systems can extract information from applications, claims forms, and policy documents in minutes rather than hours or days.
Claims processing becomes significantly faster with AI systems that can analyze photographs, read reports, and make initial assessments without human review for routine cases. Insurance staff can focus on complex cases that require human judgment while AI handles straightforward claims automatically.
Error rates drop significantly with AI systems that consistently apply business rules and regulatory requirements. Fewer errors mean reduced costs for corrections, regulatory compliance issues, and customer service problems.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Customer service response times improve dramatically with AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants that provide instant answers to common questions. Customers receive immediate responses about policy details, claims status, and billing information without waiting for human agents.
Personalized interactions become possible when AI systems analyze customer data to provide tailored recommendations and communications. Insurance companies can suggest appropriate coverage options, identify potential discounts, and proactively address customer needs.
Service availability extends beyond traditional business hours as AI systems operate continuously. Customers can submit claims, receive quotes, and access policy information at any time, improving convenience and satisfaction levels.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing artificial intelligence in insurance organizations involves navigating complex regulatory requirements, protecting sensitive customer data, and integrating new technologies with existing systems.
The insurance industry operates under strict oversight from state and federal regulators who establish specific requirements for AI system implementation. Organizations must balance innovation with compliance while ensuring their AI applications meet evolving standards for fairness and transparency.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners established comprehensive principles for AI adoption through their FACTS framework, which requires AI systems to be Fair, Accountable, Compliant, Transparent, and Secure. State insurance commissioners enforce these standards through regular examinations.
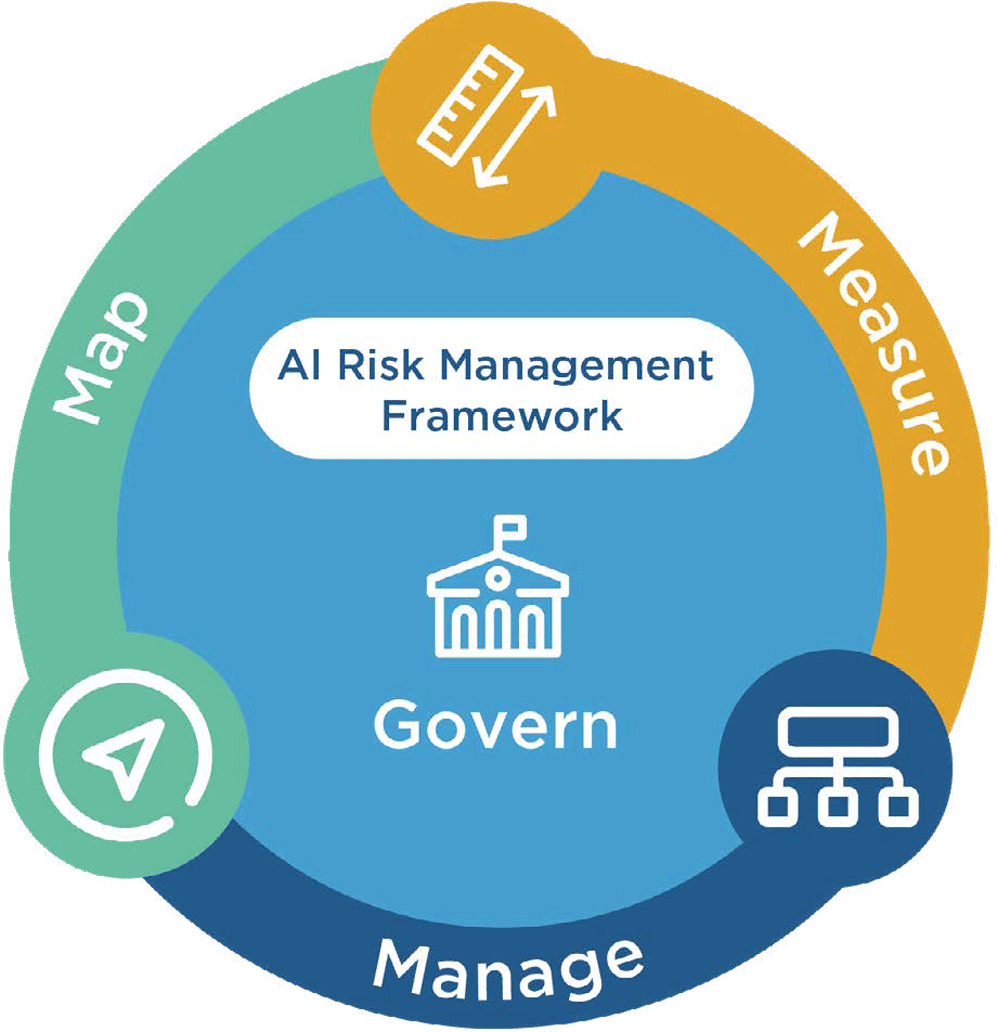
Source: Actuarial Review – Casualty Actuarial Society
Insurance companies must implement governance structures that include senior management oversight and board-level accountability for AI system decisions. The NAIC Model Bulletin requires insurers to develop comprehensive AI Systems programs with documented risk management controls.
Documentation requirements extend throughout the AI system lifecycle, from development and testing to deployment and ongoing monitoring. Companies must maintain detailed records of their risk identification processes, bias testing procedures, and mitigation strategies.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Insurance AI systems process extensive personal information including medical records, financial statements, credit histories, and behavioral data from multiple sources. The General Data Protection Regulation and various state privacy laws establish strict requirements for data collection, processing, storage, and sharing.
Data minimization principles require companies to collect only the information necessary for specific AI applications and to retain that data only as long as needed. Organizations must establish clear policies for data lifecycle management and implement automated systems for data deletion when retention periods expire.
Cybersecurity measures for AI systems require specialized approaches beyond traditional IT security protocols. AI models can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks where malicious actors manipulate input data to cause incorrect decisions or expose sensitive training information.
Future Trends in Insurance AI
The insurance industry stands at the beginning of a technological revolution that will reshape how companies operate and serve customers. Several key trends are emerging that will define the next decade of insurance technology.
Source: SmartDev
Generative AI Expansion
Generative artificial intelligence will move beyond customer service chatbots to create personalized insurance content and documents. These systems will generate customized policy documents, produce marketing materials tailored to specific customer groups, and develop new insurance product concepts based on market analysis.
The technology will also transform how insurers communicate with customers. Instead of using template responses, generative AI will create unique, personalized explanations of coverage terms, claims processes, and policy changes based on each customer’s specific situation.
Real-Time Risk Assessment
Internet of Things devices will fundamentally change how insurers assess and price risk. Smart home sensors, vehicle telematics, wearable health devices, and environmental monitoring systems will provide continuous data streams about actual risk exposure rather than historical estimates.
Home insurance policies will adjust premiums based on real-time data about property maintenance, security systems, and local weather conditions. Auto insurance will use vehicle sensors to monitor driving behavior, road conditions, and vehicle maintenance status.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Insurance
How does AI detect insurance fraud differently from traditional methods?
AI fraud detection systems analyze multiple data types simultaneously, including text, images, and behavioral patterns, to identify suspicious claims in real-time. Traditional fraud detection relied on manual review of individual claims and basic rule-based systems that flagged obvious red flags.
Machine learning algorithms can identify subtle patterns across millions of claims that human investigators would miss. These systems detect relationships between seemingly unrelated claims, unusual timing patterns, and inconsistencies in documentation that suggest coordinated fraud schemes.
What types of insurance claims can AI process automatically?
AI systems can automatically process routine claims with clear documentation and straightforward damage assessments. Auto insurance claims involving minor accidents with clear fault determination and standard repair procedures often qualify for automated processing.
Property insurance claims for common issues like roof damage from storms or appliance-related water damage can be processed automatically when customers provide clear photographs and documentation. However, complex claims involving multiple parties, severe injuries, or unusual circumstances still require human review.
How accurate are AI risk assessment models compared to human underwriters?
AI risk assessment models demonstrate higher consistency and can process more data points than human underwriters, but accuracy varies by insurance line and risk type. Studies show AI models reduce underwriting errors for routine applications while maintaining comparable accuracy to experienced underwriters for complex risks.
The combination of AI and human expertise often produces the most accurate results. AI handles data analysis and pattern recognition, while human underwriters provide judgment for unusual situations and regulatory compliance oversight.
Do customers need to interact differently with AI-powered insurance systems?
Customers typically find AI-powered insurance systems easier to use than traditional processes. Chatbots and virtual assistants respond immediately to questions and can handle multiple inquiries simultaneously without wait times.
Mobile applications with AI capabilities allow customers to submit claims by taking photographs and answering simple questions. The systems guide users through each step and provide real-time feedback about missing information or documentation requirements.
How do insurance companies ensure AI systems remain compliant with state regulations?
Insurance companies implement comprehensive AI governance frameworks that include regular algorithm audits, bias testing, and compliance monitoring. These systems automatically generate documentation required for regulatory examinations and maintain detailed logs of all AI decisions.
Compliance teams work with technical staff to ensure AI systems meet state-specific requirements for transparency, fairness, and explainability. Regular testing protocols verify that AI decisions don’t discriminate against protected classes or violate insurance regulations.
Artificial intelligence has become an essential tool for insurance companies seeking to improve operations while meeting evolving customer expectations. The technology streamlines routine processes, enhances risk assessment accuracy, and provides personalized customer experiences that weren’t possible with traditional methods. While implementation challenges exist around regulatory compliance and data security, the benefits of AI adoption continue to drive widespread transformation across the insurance industry.

