The Rome Call for AI Ethics is a global initiative launched by the Vatican in 2020 that establishes six core principles for ethical artificial intelligence development and deployment.
In February 2020, an unprecedented coalition gathered at the Vatican to address one of the most pressing challenges of our time. The Pontifical Academy for Life brought together Microsoft, IBM, the Food and Agriculture Organization, and the Italian Government to create the first major faith-based framework for AI ethics. Their collaboration produced the Rome Call for AI Ethics, introducing the concept of “algorethics” to ensure ethical considerations shape artificial intelligence from its earliest design stages.

Source: AI-PRO.org
The initiative emerged during a critical period when AI technologies began demonstrating remarkable capabilities while raising profound questions about their impact on society. Unlike purely regulatory approaches, the Rome Call grounds AI governance in fundamental principles of human dignity and the common good. For organizations seeking comprehensive responsible AI guidance, this framework provides essential ethical foundations.
What Is the Rome Call for AI Ethics
The Rome Call for AI Ethics is a voluntary ethical framework for artificial intelligence development created by the Vatican’s Pontifical Academy for Life. This global initiative brings together technology companies, governments, international organizations, and religious leaders to establish fundamental principles for responsible AI development and deployment.
The framework emerged from growing concerns about AI’s rapid advancement and potential societal impacts. Archbishop Vincenzo Paglia, who leads the Pontifical Academy for Life, recognized the urgent requirement for ethical guidance as AI technologies began affecting virtually every aspect of human life.
The Rome Call introduces the concept of “algorethics” — embedding ethical considerations into AI systems from their initial design rather than adding ethics as an afterthought. The framework establishes six core principles that guide AI development across all applications and industries.
The original signing ceremony included representatives from major technology companies and international organizations. Since its launch, the initiative has expanded significantly, with technology companies like Cisco joining in 2024 and representatives from eleven world religions signing the framework during a historic ceremony in Hiroshima, Japan in July 2024.
Six Core Principles of the Rome Call
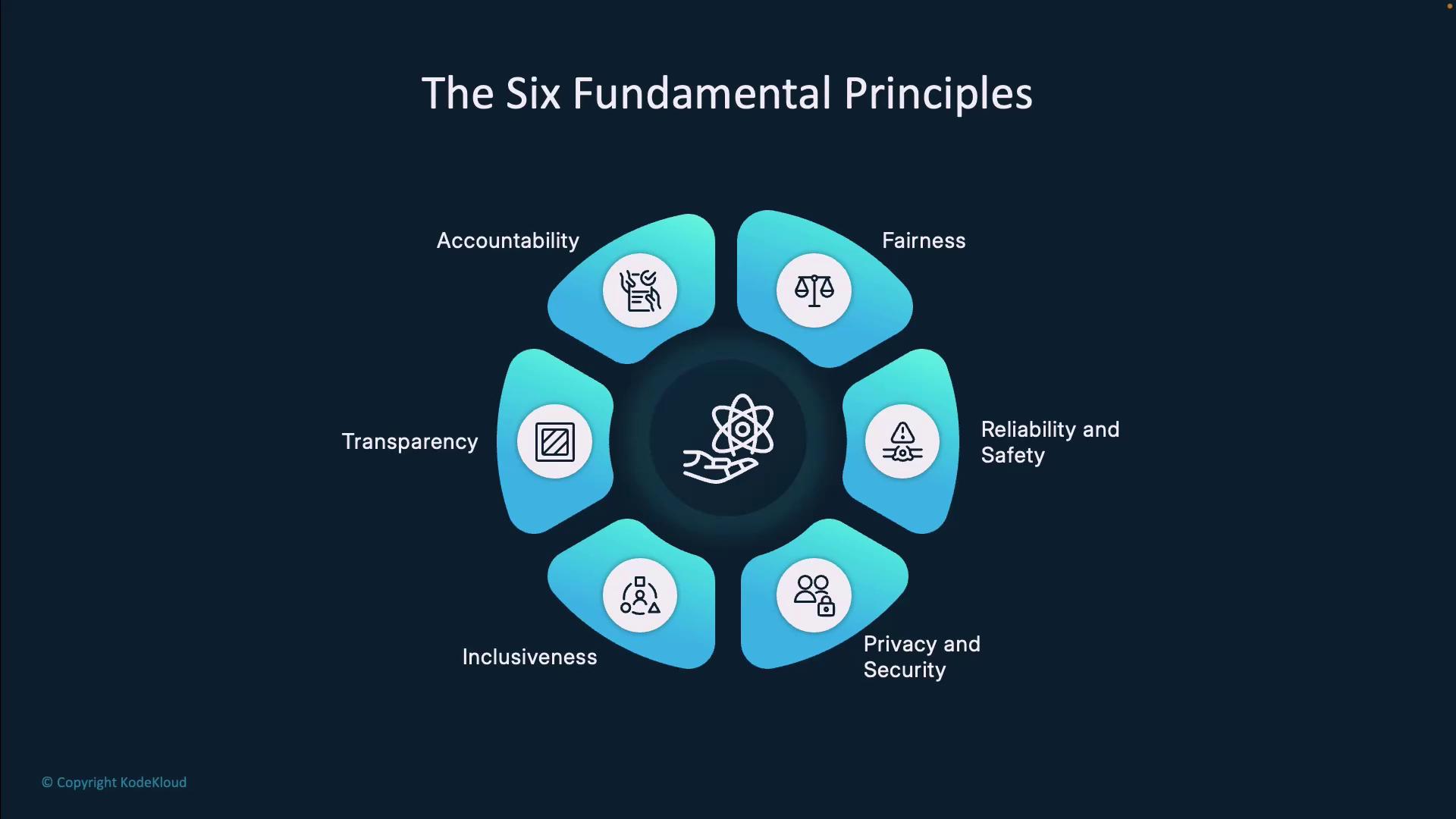
Source: KodeKloud Notes
The Rome Call establishes six foundational principles that guide ethical AI development and deployment. These principles form the “algorethics” approach — building ethical considerations into AI systems from the design phase.
Transparency
Transparency requires AI systems to be explainable and understandable to users and stakeholders. The Rome Call introduces the “duty of explanation” concept, which means people affected by AI decisions have the right to understand how those decisions were made. This principle aligns closely with explainable AI requirements that help organizations avoid black box decision-making.
Organizations implementing transparency create clear documentation about how their AI systems make decisions. For example, patients have the right to know when AI assists in medical diagnoses, job applicants can understand when AI screens resumes, and customers recognize when chatbots handle their inquiries.
Inclusion
Inclusion ensures AI technologies serve all people, with particular attention to vulnerable and marginalized populations. This principle requires active efforts to identify and prevent discriminatory outcomes rather than simply avoiding intentional bias.
Fair representation involves ensuring training data includes diverse populations and perspectives. Accessibility requirements mean AI systems work for people with disabilities, different languages, and varying technological access levels.
Responsibility
Responsibility establishes clear accountability chains for AI systems, ensuring human agents remain answerable for AI actions and decisions. The Rome Call states “there must always be someone who takes responsibility for what a machine does.”
Human oversight requirements vary by application risk level. High-stakes decisions like medical diagnoses or criminal sentencing require human review, while low-risk applications like product recommendations may operate with less direct oversight.
Impartiality
Impartiality focuses on preventing AI systems from creating or perpetuating unfair treatment based on protected characteristics like race, gender, age, or religion. This principle goes beyond avoiding discrimination to actively promoting equitable outcomes.
Neutral decision-making processes avoid favoring particular groups while considering legitimate factors relevant to decisions. For example, credit scoring systems may consider income and payment history but shouldn’t consider race or zip code as proxies for creditworthiness.
Reliability
Reliability ensures AI systems function consistently and dependably, particularly in applications where failures could cause harm. This principle encompasses both technical reliability and moral reliability — systems perform as intended and uphold ethical principles consistently.
Safety protocols establish procedures for handling system failures, monitoring for unintended consequences, and maintaining human oversight in critical applications.
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy protection addresses data protection and cybersecurity requirements throughout AI system lifecycles. This principle recognizes that AI systems often process sensitive personal information and face various security threats.
Data protection standards include encryption of stored and transmitted data, access controls limiting who can view or modify information, and data minimization practices that collect only necessary information.
Major Organizations That Have Signed the Rome Call
Source: SFB 1265
The Rome Call has attracted signatories from diverse sectors, demonstrating widespread recognition of the need for ethical AI governance. The initiative began with founding partners in February 2020 and continues expanding its coalition worldwide.
Technology industry leaders include:
- Microsoft — Brad Smith, Microsoft’s President, signed as a founding member in February 2020
- IBM — John Kelly III, former Executive Vice President, joined as an original signatory
- Cisco — Chair and CEO Chuck Robbins signed in April 2024
International organizations and government bodies provide institutional support:
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) — Director-General Qu Dongyu signed as a founding member, bringing focus to AI applications in agriculture and food security
- Italian Government — Represented by Paola Pisano at the original signing ceremony
- Vatican City State — Established comprehensive AI guidelines in 2025 that serve as implementation models
The Rome Call achieved remarkable multi-religious engagement during the “AI Ethics for Peace” event in Hiroshima, Japan, in July 2024. Representatives from eleven world religions signed the framework, including Buddhist, Hindu, Islamic, Jewish, and other religious traditions.
How the Rome Call Differs From Other AI Ethics Frameworks
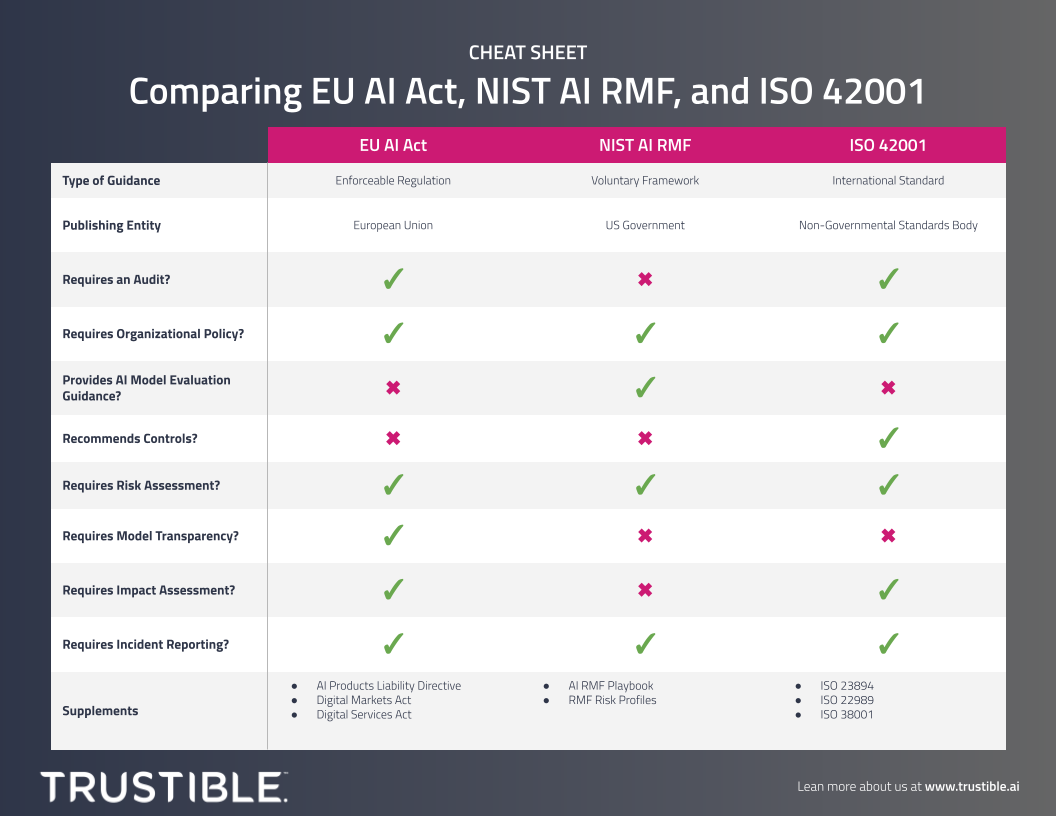
Source: Trustible AI
The Rome Call occupies a unique position among global AI governance frameworks by combining religious perspectives with technological oversight. While other frameworks focus primarily on technical standards or regulatory compliance, the Rome Call emphasizes human dignity and universal moral principles.
The EU AI Act represents legally binding requirements for AI systems deployed in European markets, while the Rome Call operates as a voluntary ethical framework. The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems by risk level and imposes strict oversight requirements for high-risk systems. The Rome Call applies its six principles universally across all AI applications.
IEEE’s Ethically Aligned Design standards approach AI ethics through engineering methodology and technical specifications. The Rome Call grounds AI ethics in theological and philosophical principles of human dignity rather than technical requirements. Organizations can complement these approaches with ISO 42001 implementation for comprehensive governance.
Industry-led frameworks like the Partnership on AI emphasize business sustainability and competitive considerations alongside ethical concerns. The Rome Call prioritizes universal human values independent of commercial interests or specific business contexts.
Implementing Rome Call Principles in Organizations
Source: LinkedIn
Organizations can implement Rome Call principles through structured approaches that translate abstract ethical concepts into concrete operational practices. Implementation varies by organization size and existing AI capabilities.
Small organizations often begin with basic transparency measures like clearly labeling AI-generated content and informing customers when AI systems are involved in business processes. They can designate specific staff members to oversee AI usage and establish clear decision-making chains. For companies deploying AI agents in customer service, these transparency requirements become particularly important for maintaining customer trust.
Larger enterprises typically invest in dedicated ethics boards, specialized software tools for AI monitoring, and comprehensive staff education programs across multiple departments. They develop written policies that translate each Rome Call principle into specific organizational requirements. Retail organizations implementing AI in retail environments must consider transparency in recommendation systems and fairness in pricing algorithms.
The Vatican’s implementation guidelines demonstrate practical application of these principles. Vatican City State established a five-person AI commission to oversee AI implementation and created specific requirements for different operational contexts:
- Healthcare guidelines — Mandate explicit patient notification about AI involvement in care
- Judicial guidelines — Prohibit AI from making legal interpretations or sentencing decisions
- Content requirements — All AI-generated content must be immediately recognizable to users
Organizations seeking professional guidance can benefit from AI consulting services that help translate Rome Call principles into sector-specific implementations.
Recent Developments and Global Impact

Source: Osservatore Romano
The Rome Call continues evolving through strategic partnerships and practical implementations across diverse sectors. The Hiroshima Addendum specifically addresses generative AI applications, updating the original principles for emerging technologies like large language models. This development recognizes the distinctions between generative AI and predictive AI applications.
Academic institutions worldwide have incorporated the Rome Call’s principles into their AI research and education programs. The Global University Summit for the Rome Call brings together educational leaders to develop curricula that integrate ethical AI principles into technology education.
Sector-specific applications continue developing in agriculture, healthcare, and other critical areas. The Food and Agriculture Organization applies Rome Call principles to AI systems that monitor agricultural water productivity, detect drought conditions, and track forest changes.
The RenAIssance Foundation, established by Pope Francis as the institutional vehicle for promoting the Rome Call, coordinates activities among signatories and develops practical guidance for implementing ethical AI practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the Rome Call for AI Ethics legally binding?
No, the Rome Call for AI Ethics is not legally binding. Organizations that sign the Rome Call make a voluntary moral commitment to follow its six core principles. The framework relies on good faith implementation by signatories rather than legal enforcement mechanisms.
How much does implementing Rome Call principles cost organizations?
Implementation costs vary significantly based on organization size, existing AI capabilities, and the scope of AI systems being deployed. Organizations typically face expenses in staff training, governance structure development, technical modifications for transparency and bias detection, and ongoing monitoring activities.
Can small businesses adopt the Rome Call framework effectively?
Yes, small businesses can adopt the Rome Call framework by focusing on scalable implementations. They often begin with transparency measures like labeling AI-generated content and designating staff to oversee AI usage, gradually expanding their ethical AI practices as resources allow. AI consulting services can help small businesses develop cost-effective implementation strategies.
What happens if an organization violates Rome Call principles after signing?
No formal legal consequences exist for violating Rome Call principles since the framework operates on voluntary commitment. However, organizations may face reputational damage, public criticism, and loss of stakeholder trust when their AI practices contradict their stated commitments.
The Rome Call for AI Ethics represents a groundbreaking approach to AI governance that combines moral authority with practical guidance. As AI continues transforming society, this framework provides organizations worldwide with principles that prioritize human dignity while fostering technological innovation. The initiative’s expansion from Vatican origins to global multi-religious participation demonstrates the universal relevance of ethical AI development.



