Artificial intelligence return on investment (ROI) measures the financial value organizations gain from AI investments compared to implementation costs.
The AI market reached a critical turning point in 2025, with organizations shifting from experimental pilots to enterprise-wide deployments that demand measurable returns. Recent research from the IBM Institute reveals a stark divide: top-performing organizations achieve approximately 18 percent ROI on AI initiatives, while most enterprises struggle to demonstrate tangible business value. This performance gap highlights the urgent need for strategic approaches that move beyond initial AI excitement toward systematic methodologies.

Organizations that succeed in maximizing AI returns adopt comprehensive governance frameworks, implement rigorous measurement systems, and align AI strategies with core business objectives rather than peripheral experiments. The transition from innovation budgets to core IT expenditures reflects organizational maturation but raises stakes for demonstrating concrete business value.
Understanding AI ROI and Why It Matters
AI ROI measures the business value organizations gain from artificial intelligence investments compared to the costs of implementing and maintaining those systems. Unlike traditional technology investments that typically automate existing processes, AI can fundamentally change how organizations operate, make decisions, and serve customers.
Traditional ROI calculations often miss AI's full impact because they focus on immediate, measurable returns while overlooking long-term transformational benefits. AI investments create value through multiple channels that extend beyond simple cost-benefit analysis.
The measurement challenge becomes more complex because AI often improves organizational capabilities rather than just individual processes. Enhanced data insights may lead to better strategic decisions across multiple departments. Improved customer experience through AI can increase retention and referrals in ways that are difficult to attribute directly to the original AI investment.
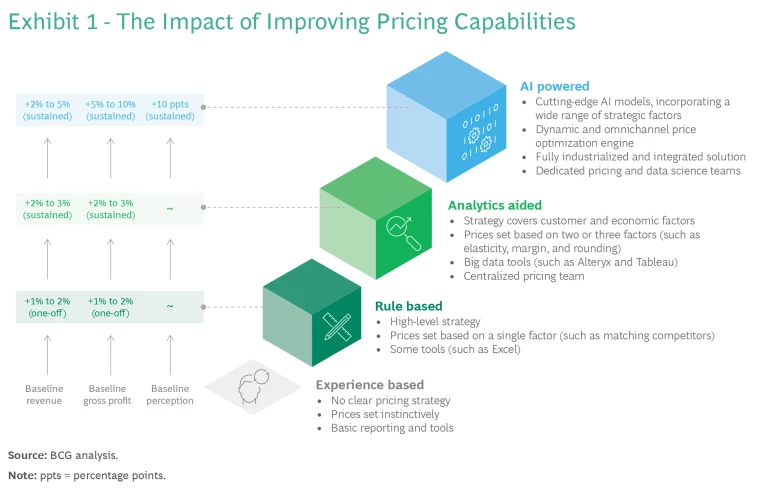
AI creates value through these key areas:
- Revenue growth — New products and services enabled by AI capabilities, improved sales targeting through AI agents in sales, dynamic pricing optimization
- Cost reduction — Automated processes replacing manual work, reduced error rates, optimized resource allocation through supply chain AI
- Efficiency gains — Faster processing times, improved accuracy, reduced waste in operations
- Market positioning — Differentiation through AI-powered features, faster innovation cycles, enhanced competitive intelligence
Developing Your AI Investment Strategy
Creating an AI investment plan starts with business objectives rather than available technology. Companies achieve better returns when they identify specific business problems first, then evaluate how AI might solve them. This approach prevents organizations from implementing AI solutions searching for problems to solve.
Executive leadership support drives successful AI implementations across departments. When CEOs and senior managers actively participate in AI strategy development, projects receive adequate resources and organizational commitment. Cross-functional teams that include representatives from finance, operations, IT, and affected business units create more comprehensive plans that address real operational challenges.
Finding High-Value AI Use Cases
Organizations evaluate potential AI applications using three primary criteria: business impact, technical feasibility, and resource requirements. Business impact measures how significantly an AI solution could improve revenue, reduce costs, or enhance customer experience. Technical feasibility assesses whether current technology and data can support the proposed solution.

Successful organizations examine their current processes to identify repetitive tasks, data-rich decisions, or customer interactions that could benefit from automation or enhancement. Manufacturing companies might focus on quality control processes, while retail organizations could prioritize inventory management or customer service applications.
Building Strong Business Cases
Business cases for AI investments require quantification of both tangible and intangible benefits. Tangible benefits include direct cost savings from automation, increased revenue from improved customer targeting, or reduced errors in decision-making processes. Organizations calculate these benefits using baseline measurements of current performance and projected improvements from AI implementation.
Intangible benefits encompass improved customer satisfaction, enhanced decision-making speed, or competitive advantages from new capabilities. While harder to quantify, these benefits often represent significant long-term value. Companies present intangible benefits using industry benchmarks, customer feedback data, or competitive analysis that demonstrates strategic importance.
Implementation costs include technology acquisition, data preparation, system integration, training, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Organizations often underestimate the time and resources required for data cleaning and system integration. Realistic timelines account for data preparation phases, pilot testing periods, and gradual rollout across business units.
Essential AI Governance for Better Returns
AI governance forms the backbone of sustainable return on investment by establishing the processes, policies, and oversight mechanisms that ensure AI systems operate responsibly, comply with regulations, and scale effectively across organizations. Governance frameworks provide structure for managing AI development, deployment, and maintenance while protecting organizations from risks that could undermine their technology investments.

Effective AI governance encompasses multiple interconnected components that work together to create comprehensive oversight. Regulatory compliance ensures adherence to evolving legal requirements across different jurisdictions. Risk management identifies and mitigates potential operational, financial, and reputational hazards.
Managing Risk and Compliance
Regulatory requirements for AI systems have expanded dramatically. Organizations face compliance obligations spanning data privacy, algorithmic fairness, transparency, and accountability across multiple jurisdictions with varying requirements. Financial services organizations must address regulations from banking authorities regarding algorithmic decision-making in lending and risk assessment.
Implementing NIST AI RMF provides a structured approach to managing these compliance requirements. Audit trails form a critical component of compliance frameworks by documenting AI system development, training data sources, model performance metrics, and decision-making processes.
Risk mitigation strategies address both technical and operational hazards that could impact AI system performance or create liability exposure:
- Technical risks — Model drift, where AI performance degrades over time due to changing data patterns, and adversarial attacks designed to manipulate AI outputs
- Operational risks — Inadequate training leading to user errors, insufficient monitoring causing undetected failures, and integration problems disrupting business processes
- Financial risks — System failures, regulatory penalties, and business interruption scenarios requiring comprehensive insurance evaluation
Implementing Ethical AI Practices
Ethical AI implementation extends beyond regulatory compliance to address fairness, transparency, and accountability considerations that affect stakeholder trust and long-term system viability. Responsible AI practices help organizations build systems that create value while minimizing potential harm.
Bias detection and mitigation processes identify and correct discriminatory patterns in AI training data and algorithmic decision-making. Statistical testing measures algorithmic outcomes across different demographic groups to identify disparate impact patterns.
Transparency requirements vary based on AI application context and stakeholder needs. High-impact decisions affecting employment, lending, or legal proceedings typically require explainable AI approaches that can articulate reasoning behind algorithmic recommendations. Explanation systems provide different levels of detail for technical users, business stakeholders, and affected individuals.
Choosing the Right Technology Solutions
The artificial intelligence technology landscape in 2025 presents organizations with an unprecedented array of deployment options, vendor choices, and cost optimization strategies. The key to maximizing value lies in making strategic decisions based on business requirements rather than pursuing the latest technological trends.
AI Infrastructure Options
Organizations face three primary infrastructure approaches when deploying AI systems: cloud-based platforms, on-premises solutions, and hybrid architectures. Each approach offers distinct advantages and challenges that directly impact long-term return on investment.

Cloud-based AI platforms provide immediate access to advanced computing resources without significant upfront capital investment. Major providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer specialized AI services including pre-trained models, machine learning platforms, and automated scaling capabilities.
On-premises solutions give organizations complete control over their AI infrastructure and data. This approach appeals to companies with strict security requirements, regulatory compliance needs, or existing data center investments. On-premises deployments require substantial upfront hardware investments but offer predictable long-term costs and maximum customization flexibility.
Hybrid approaches combine cloud and on-premises resources to optimize both performance and cost. Organizations typically use cloud resources for development and training while deploying production workloads on-premises for security or latency requirements.
Vendor Selection Criteria
Effective vendor evaluation requires a structured framework that assesses multiple dimensions of capability and compatibility. Technical capabilities form the foundation of vendor assessment, including the breadth of AI services offered, model performance benchmarks, and platform integration features.
Model performance varies significantly across vendors and use cases. Organizations benefit from conducting proof-of-concept evaluations using their actual data and requirements rather than relying solely on published benchmarks. Performance testing helps identify which vendors deliver superior results for specific business applications.
Support quality determines how quickly organizations can resolve issues and implement new capabilities:
- Response time commitments — Clear service level agreements for technical support
- Technical expertise availability — Access to specialized knowledge for complex implementations
- Documentation quality — Comprehensive guides and troubleshooting resources
- Training resources — Educational materials and certification programs
Implementing AI for Maximum Value
Successful AI implementation requires strategic planning that connects technology capabilities with business objectives. Organizations achieving strong returns focus on three core areas: technical integration, data quality, and organizational change management.

The foundation of effective AI implementation lies in systematic approaches that address both technical requirements and human factors. Teams that deliver measurable results typically establish clear governance structures, implement robust testing protocols, and maintain continuous improvement processes throughout the AI lifecycle.
Enterprise Integration Best Practices
AI systems perform best when they connect seamlessly with existing technology infrastructure. Organizations start by conducting comprehensive architecture assessments that map current systems, data flows, and integration points before implementing AI solutions.
The integration process begins with evaluating existing APIs, databases, and middleware that will interact with AI components. Teams identify potential bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and performance constraints that could impact AI system effectiveness.
Modern AI integration often requires hybrid architecture approaches that combine cloud resources with on-premises systems. Cloud platforms provide scalable computing power for AI training and complex processing, while local systems maintain control over sensitive data and mission-critical operations.
Data Management Essentials
Data quality directly determines AI system performance and business value creation. Organizations implement comprehensive data management frameworks that address collection, validation, storage, and governance throughout the AI development process.
Data preparation begins with identifying relevant data sources across the organization. Teams catalog existing databases, document repositories, and external data feeds that contain information relevant to specific AI use cases. This inventory process reveals data gaps and quality issues that require attention before AI implementation.
Quality assurance processes include automated validation checks that identify incomplete records, inconsistent formats, and duplicate entries. Teams establish data cleansing procedures that standardize formats, resolve conflicts, and fill missing values using statistical methods or business rules.
Measuring AI Performance and ROI
Measuring AI performance requires structured frameworks that track both technical metrics and business outcomes. Organizations use multiple measurement approaches to understand whether their AI investments create real value and where improvements can be made.
ROI Calculation Methods
Time-based ROI calculations measure how quickly AI systems deliver returns compared to initial investments. Organizations typically track payback periods ranging from six months for simple automation projects to 24-plus months for complex enterprise implementations. Monthly tracking reveals whether systems meet projected timelines and helps identify delays that might impact overall returns.
Efficiency metrics compare pre-AI and post-AI performance across key processes. Organizations measure percentage improvements in task completion times, error reduction rates, and resource utilization. A customer service AI might reduce average call resolution time from eight minutes to three minutes, representing a 62 percent efficiency gain that translates directly to cost savings.
Business outcome frameworks connect AI performance to revenue, cost reduction, and competitive positioning. Organizations track metrics like customer acquisition cost changes, revenue per employee improvements, and market share shifts attributable to AI capabilities.
Key Performance Indicators
Different AI implementations require specific KPI frameworks that align with their intended business outcomes. Organizations typically track three categories of metrics across their AI portfolio.
Operational KPIs measure direct system performance:
- Processing time reduction — How much faster AI systems complete tasks compared to manual processes
- Error rate decrease — Reduction in mistakes, defects, or incorrect outputs after AI implementation
- Throughput improvements — Increases in volume of work completed per time period
Financial KPIs connect AI performance to business results:
- Cost per transaction — Total cost to complete individual business transactions using AI systems
- Revenue attribution — Revenue directly generated or influenced by AI capabilities
- Margin improvements — Profit margin changes resulting from AI-driven cost reductions or revenue increases
Optimizing AI Costs and Resources
Managing AI costs effectively requires understanding expenses across the entire project lifecycle, from initial development through ongoing operations. Organizations typically allocate between $50,000 and $500,000 annually for enterprise AI initiatives, with costs varying significantly based on complexity, data requirements, and deployment scale.
AI expenses fall into several categories: computational infrastructure, software licensing, data acquisition and preparation, personnel costs, and ongoing maintenance. Computational costs often represent 40 to 60 percent of total AI budgets, particularly for training large models or processing substantial data volumes.
Budget Management Strategies
AI budget planning begins with establishing clear financial boundaries for each project phase. Development phases require different resource allocations than production deployment, with training typically consuming more computational resources than inference operations.
Cost allocation methods vary by organization structure and project type. Some companies allocate AI costs as shared services across business units, while others assign expenses directly to specific departments or product lines. The allocation method affects how teams measure return on investment and make resource decisions.
Financial controls for AI projects include spending caps for computational resources, approval processes for additional data purchases, and regular budget reviews to track actual versus projected expenses. Many organizations implement automated spending alerts when cloud computing costs exceed predetermined thresholds.
Resource Optimization Techniques
Computational resource optimization starts with selecting appropriate hardware and cloud services for specific workloads. Training models requires different resources than running inference, with GPU-intensive training often benefiting from cloud bursting while production inference may work better with dedicated infrastructure.

Model optimization techniques can reduce computational requirements by 50 to 80 percent without significant performance loss:
- Quantization — Reduces model precision from 32-bit to 8-bit or 16-bit, decreasing memory usage and improving inference speed
- Pruning — Removes unnecessary model parameters, creating smaller, faster models that maintain accuracy
- Knowledge distillation — Creates smaller, faster models that approximate the performance of larger systems
Cloud cost optimization involves selecting appropriate instance types, utilizing spot instances for non-critical workloads, and implementing automatic scaling to match resource consumption with actual demand. Reserved instances can provide 30 to 60 percent cost savings for predictable workloads compared to on-demand pricing.
Building Long-Term AI Success
Organizations pursuing artificial intelligence initiatives often achieve better results when they work with experienced consultants and technology providers rather than attempting implementation alone. Strategic partnerships bring specialized expertise, proven methodologies, and established best practices that can significantly accelerate time-to-value while reducing common implementation risks.
The AI skills shortage continues to challenge companies across all sectors, making it difficult to build comprehensive internal capabilities quickly enough to meet business objectives. External partners can supplement internal teams with specific expertise while also providing knowledge transfer that builds long-term organizational capabilities.
Strategic partnerships also provide access to proven governance frameworks, established security practices, and comprehensive compliance knowledge. Experienced partners understand regulatory requirements across different industries and can help organizations implement appropriate controls from the beginning rather than retrofitting compliance capabilities later.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI ROI
How long does it take to see returns from AI investments?
AI return on investment timelines depend heavily on the type and scope of the project being implemented. Simple automation projects, such as chatbots for basic customer service or document processing systems, typically deliver measurable returns within three to six months of deployment. These projects focus on replacing repetitive manual tasks with automated processes, making their benefits relatively easy to track and quantify.
More complex AI initiatives, such as predictive analytics systems or comprehensive process transformation projects, generally require 12 to 24 months before organizations see full value realization. Research shows that while early pilot programs often demonstrate impressive returns, these numbers typically decline as projects scale to enterprise-wide implementations due to integration challenges and organizational adaptation requirements.
What percentage of budget should companies allocate to AI initiatives?
AI budgeting strategies vary based on organizational size, industry, and AI maturity level. Organizations typically begin with pilot projects that represent one to three percent of their total IT budget to test concepts and build internal capabilities before committing larger resources to scaled implementations.
As AI programs mature, companies often allocate between five to 15 percent of their technology budgets to AI initiatives. Organizations achieve better returns when they allocate budgets across three categories: foundational infrastructure (40 to 50 percent), core business applications (30 to 40 percent), and experimental projects (10 to 20 percent).
Should organizations build AI capabilities internally or work with external partners?
The build-versus-partner decision depends on several organizational factors. Companies with strong technical teams and substantial AI experience often develop capabilities internally to maintain control over intellectual property and build long-term competitive advantages. Internal development works best when organizations have dedicated data science teams, robust IT infrastructure, and clear AI strategy alignment.
Many organizations find success with hybrid approaches that combine internal teams with external expertise. This model allows companies to leverage specialized knowledge for complex implementations while building internal capabilities over time. Organizations with limited technical resources or tight timelines typically benefit more from consultant partnerships, especially for initial AI initiatives.
What are the most common causes of poor AI ROI performance?
Poor data quality represents the most significant threat to AI return on investment. AI systems perform only as well as the data they process, and organizations with fragmented, inconsistent, or inaccurate data sources often struggle to achieve expected results. Data integration challenges and quality issues can delay implementation timelines and reduce system effectiveness.
Inadequate change management undermines many AI initiatives, even when the technology performs as designed. Employees may resist new systems, lack proper training, or continue using legacy processes, preventing organizations from realizing anticipated productivity gains. Unrealistic expectations about AI capabilities also create ROI risks when stakeholders expect immediate transformational results from complex implementations.
How should companies evaluate underperforming AI projects?
Underperforming AI projects require systematic evaluation to determine appropriate next steps. Organizations start by reviewing original project objectives and success metrics to verify whether expectations were realistic and properly aligned with business goals. This analysis includes examining whether the project addressed the right business problem and whether success criteria were appropriately defined and measurable.
Implementation quality assessment examines technical factors such as data quality, model performance, user adoption rates, and integration effectiveness. Many projects fail due to execution issues rather than fundamental strategy problems, making implementation review a critical diagnostic step. Based on this analysis, organizations typically choose from three options: strategic adjustments to address identified issues, project continuation with modified scope or approach, or project termination when fundamental assumptions prove invalid.

