AI agents in customer service are intelligent software systems that handle customer inquiries, resolve issues, and provide support without human intervention by using natural language processing and machine learning.
Customer service operations face mounting pressure to deliver faster responses while managing costs. Traditional call centers struggle with staffing challenges, long wait times, and inconsistent service quality across different shifts and locations. Meanwhile, customers expect immediate assistance available around the clock.
AI agents transform this landscape by providing instant responses to customer questions at any time of day. These systems understand natural language, access customer data, and solve problems autonomously. Unlike simple chatbots that follow scripts, modern AI agents reason through complex situations and make decisions based on context.
The technology has reached a maturity level where organizations report significant operational improvements. Implementation timelines have shortened from months to weeks as the technology becomes more accessible and integration tools improve.
What Are AI Agents in Customer Service
AI agents in customer service are autonomous software programs that can understand, process, and respond to customer inquiries without requiring human intervention. These systems operate independently to handle customer questions, solve problems, and complete tasks by analyzing what customers say or type and generating appropriate responses.
AI agents use machine learning algorithms to improve their responses over time by learning from previous interactions. They rely on natural language processing technology to understand human language in its various forms, including slang, different sentence structures, and context clues that help determine what customers actually want or need.
Core AI Agent Capabilities
AI agents possess several key capabilities that enable them to provide effective customer service:
- Natural language understanding — Interprets customer messages written in everyday language, including questions with spelling errors, incomplete sentences, or unclear phrasing
- Knowledge base access — Retrieves relevant information from company databases, product manuals, policy documents, and frequently asked questions in real-time
- Contextual memory — Remembers previous parts of conversations and references earlier interactions to maintain continuity throughout customer exchanges
- Multi-channel communication — Operates simultaneously across email, chat windows, social media platforms, and mobile applications
- Intent recognition — Identifies what customers want to accomplish, whether they’re asking for information, reporting problems, or requesting specific actions
AI Agents vs Traditional Chatbots
Traditional chatbots and AI agents differ significantly in their capabilities and approaches to customer service. Traditional chatbots operate like digital flowcharts, guiding customers through predetermined conversation paths based on keyword matching. AI agents function more like digital employees who can understand customer intent, access relevant information, and formulate helpful responses even for questions they haven’t encountered before.

Source: AI Chatbot for Customer Support
The key differences include response flexibility, learning capabilities, and problem-solving approaches. While chatbots follow rigid scripts, AI agents adapt conversations based on customer needs and can reason through complex problems to suggest solutions.
Benefits of AI Agents for Customer Service Operations
AI agents deliver measurable business advantages that directly impact operational costs, service availability, response efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Organizations implementing these systems report significant improvements across multiple performance metrics while maintaining service quality standards.
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency
AI agents reduce labor costs by automating routine customer inquiries that traditionally require human staff. Organizations report thirty percent reductions in overall support costs through automated handling of frequently asked questions, basic troubleshooting, and standard account inquiries.
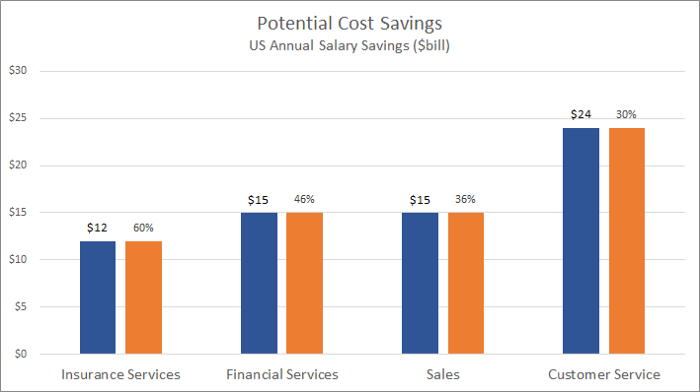
Source: ProProfs Help Desk
Human agents become available for complex problem-solving and relationship-building activities when AI handles routine tasks. This division of labor maximizes the value of human agents while containing operational costs. Small businesses particularly benefit from these efficiency gains.
24/7 Customer Support Availability
AI agents provide continuous customer service coverage across all time zones without additional staffing costs. Global organizations serve international customers without maintaining call centers in multiple regions while maintaining consistent service standards across all markets.

Source: Zendesk
Emergency and urgent inquiries receive immediate attention outside normal business hours. AI agents can escalate critical issues to on-call human staff when necessary while handling non-urgent matters independently.
Improved Response Times and Resolution Rates
AI agents provide instant responses to customer inquiries, eliminating wait times associated with queue management and agent availability. First contact resolution rates improve when AI agents access complete customer histories and knowledge bases simultaneously.
Query processing speed increases through parallel handling of multiple customer conversations. Unlike human agents who manage one interaction at a time, AI systems process numerous simultaneous requests while maintaining response quality.
How AI Agents Work in Customer Service Environments
AI agents combine three core technologies: machine learning, natural language processing, and automation. Machine learning allows AI agents to recognize patterns in data and improve their responses over time. Natural language processing enables AI agents to understand human language the way people naturally speak or write. Automation handles the execution of tasks once the AI agent determines what action to take.
When a customer sends a message, the AI agent first breaks down the text into smaller components to understand its meaning. The system identifies keywords, analyzes sentence structure, and determines the customer’s intent — whether they want to make a complaint, ask a question, or request help with a specific problem.

Source: Medium
Integration with Knowledge Bases and CRM Systems
AI agents connect directly to company databases that store product information, policies, and frequently asked questions. When a customer asks about return policies or product specifications, the agent queries these knowledge bases in real-time to retrieve current, accurate information.
Customer Relationship Management systems provide AI agents with individual customer history, including previous purchases, past support tickets, and account status. This integration allows the agent to personalize responses and understand the full context of the customer’s relationship with the company. Proper AI data management ensures these systems work seamlessly together.
Automated Workflow and Escalation Processes
AI agents follow predefined rules to determine when situations require human assistance. The system evaluates factors like conversation complexity, customer emotion indicators, and the type of request to decide whether to continue handling the interaction or transfer it to a human agent.
When escalation occurs, the AI agent packages all conversation history and relevant customer information to provide context for the human agent. For routine tasks, AI agents can trigger automated business processes without human involvement, such as processing returns or updating account information.
Implementation Strategies for AI Agents
Organizations across industries integrate AI agents into their customer service operations through systematic planning and gradual scaling. Implementation success depends on careful assessment, testing, and optimization that builds organizational confidence while minimizing disruption to existing operations.
Assessment and Planning Phase
The assessment phase begins with evaluating current customer service processes to understand interaction volumes, types of inquiries, and existing pain points. Organizations typically analyze call logs, chat transcripts, and support tickets from the past twelve months to identify patterns in customer questions and issues.
Common use cases for initial AI agent deployment include password resets, order status inquiries, basic product information requests, and frequently asked questions about policies or procedures. Setting implementation goals involves defining specific, measurable outcomes such as reducing average response time or achieving deflection rates for routine inquiries.
Pilot Program Development
Pilot programs typically start with one specific customer service channel and a limited set of interaction types. Organizations often choose email support or web chat for initial testing because these channels allow for easier monitoring and intervention if issues arise.
Testing scenarios focus on the most common, straightforward customer inquiries that represent sixty to eighty percent of total support volume. Pilot programs usually run for thirty to ninety days with small customer segments.
Full-Scale Deployment and Optimization
Expanding successful pilots involves gradually increasing the types of interactions AI agents handle and extending coverage to additional customer service channels. Organizations typically add new interaction categories monthly, starting with variations of successful pilot scenarios.
Continuous improvement involves analyzing interaction data to identify opportunities for enhancing AI agent responses, expanding knowledge bases, and refining decision-making algorithms. Organizations typically review performance data monthly and implement improvements quarterly. An AI Center of Excellence can help coordinate these optimization efforts across the organization.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Enterprise organizations deploying AI agents for customer service face complex security and compliance requirements that protect customer data while enabling effective automated support. These requirements span multiple regulatory frameworks and industry standards.
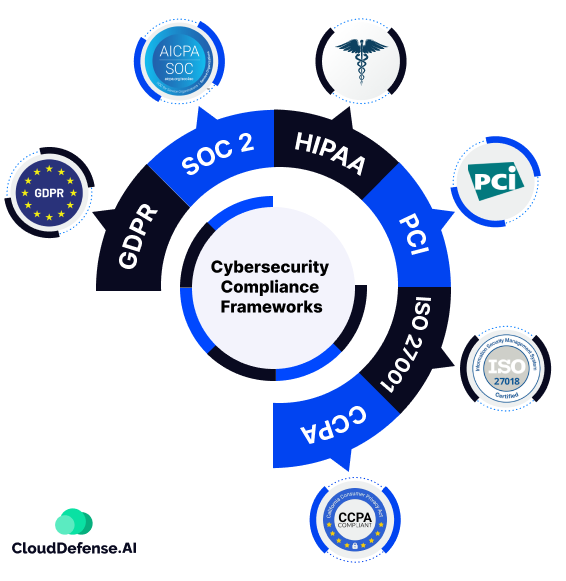
Source: CloudDefense.AI
Data Protection and Privacy Requirements
The General Data Protection Regulation establishes comprehensive privacy requirements for AI agents processing personal data of European Union residents. GDPR requires explicit customer consent for data processing, clear disclosure of AI involvement in customer interactions, and robust mechanisms for customers to access, correct, or delete their personal information.
The California Consumer Privacy Act grants California residents specific rights regarding their personal information, including the right to know what data companies collect and the right to delete personal information. Additional privacy regulations like HIPAA impose stricter requirements for healthcare-related customer data.
Industry-Specific Compliance Standards
Financial services organizations deploying AI agents comply with regulations like the Fair Credit Reporting Act and Equal Credit Opportunity Act that govern automated decision-making systems. Healthcare organizations face HIPAA requirements that mandate comprehensive safeguards for protected health information processed by AI agents.
Telecommunications companies deploying AI agents comply with Federal Communications Commission regulations regarding customer privacy and accessibility. Retail organizations consider Federal Trade Commission guidelines on fair and deceptive practices. Organizations can implement ISO 42001 standards to ensure proper AI governance.
Best Practices for Customer Service AI Agent Deployment
Successful AI agent deployment requires systematic planning and execution across multiple dimensions. Organizations achieve better outcomes when they follow proven methodologies that balance technical implementation with operational considerations.
Training and Optimization Strategies
Initial agent training requires comprehensive datasets that reflect real customer interactions and business-specific terminology. Training data encompasses customer conversation histories, product documentation, policy guidelines, and frequently asked questions across different service categories.
Ongoing learning frameworks enable continuous improvement through systematic feedback collection and model updates. These frameworks capture customer satisfaction ratings, interaction outcomes, resolution accuracy, and escalation patterns to identify improvement opportunities.
Human-AI Collaboration Models
Hybrid service models leverage AI agents for initial customer contact and routine inquiries while reserving complex issues for human agents. Escalation criteria define when AI agents transfer conversations to humans based on factors like emotional indicators, request complexity, or specific keywords that signal specialized assistance requirements.

Source: ResearchGate
Quality assurance processes evaluate both AI performance and human-AI collaboration effectiveness. Metrics include escalation decision quality, handoff smoothness, and customer satisfaction with hybrid service delivery.
Choosing the Right AI Agent Platform
Selecting an AI agent platform requires systematic evaluation of technical capabilities, business requirements, and organizational readiness. Organizations face multiple options ranging from comprehensive enterprise platforms to specialized solutions targeting specific customer service functions.
Source: QAwerk
Platform selection impacts implementation timeline, integration complexity, and ongoing operational costs. Organizations typically evaluate solutions based on technical architecture, vendor stability, support quality, and total cost of ownership across multi-year deployments.
Enterprise AI Agent Solution Evaluation
Technical evaluation begins with assessing core platform capabilities including natural language processing accuracy, integration flexibility, and scalability limits. Platforms vary significantly in their ability to handle complex conversations, maintain context across interactions, and integrate with existing enterprise systems.
Integration capabilities determine how effectively AI agents can access customer data, update records, and coordinate with human agents. Evaluation criteria include API quality, data security protocols, and compatibility with existing customer relationship management, ticketing, and knowledge management systems. Generative AI development services can help customize platforms to specific organizational needs.
Getting Started with AI Agents
Organizations ready to implement AI agents can begin with focused pilot programs that target specific customer service scenarios. These pilots provide opportunities to validate technical approaches, test integration strategies, and build organizational expertise while limiting operational risk.
Success begins with identifying specific use cases where AI agents create immediate value. Common starting points include routine inquiries like password resets, order status checks, and basic troubleshooting that currently consume substantial human agent time.
Technical implementation requires integration with existing customer relationship management systems, knowledge bases, and communication platforms. The architecture supports real-time data access while maintaining security protocols and privacy compliance standards.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Agents in Customer Service
How do AI agents handle customer data privacy and security?
AI agents protect customer data through encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. The systems process personal information according to established privacy policies and provide customers with rights to access, correct, or delete their data. Organizations implement audit trails and monitoring systems to track data access and usage patterns.
Security protocols include multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and network security measures that defend against cyber threats. Data encryption protects information both in transit and at rest, while secure coding practices prevent vulnerabilities in AI agent applications.
Can AI agents integrate with existing customer service software?
Modern AI agents integrate with popular customer service platforms including Salesforce, Zendesk, ServiceNow, and Microsoft Dynamics through application programming interfaces. These integrations enable real-time access to customer records, automatic ticket creation, and seamless handoffs to human agents when escalation occurs.
Integration capabilities vary by platform, with some offering pre-built connectors while others require custom development work. Organizations evaluate integration complexity during the vendor selection process to understand implementation requirements and timeline expectations.
What happens when AI agents cannot resolve customer issues?
AI agents seamlessly escalate unresolved issues to human agents, providing complete conversation history and customer context for smooth handoffs. The escalation process eliminates the need for customers to repeat their issues and maintains conversation continuity.
Escalation triggers include customer requests for human assistance, detection of emotional distress, identification of issues beyond the agent’s capabilities, or failure to resolve problems within predetermined parameters. Organizations establish clear escalation criteria and train human agents to handle transferred conversations effectively.
How long does AI agent implementation take for small businesses?
Small business implementations typically complete within six to twelve weeks, depending on integration complexity and existing system compatibility. Organizations with modern cloud-based software generally experience faster implementations than those requiring extensive legacy system modifications.
The timeline includes initial setup, data integration, testing, and staff training phases. Simple implementations with basic integration can launch in four to six weeks, while more complex deployments with custom requirements may extend to three months.
Do customers prefer AI agents or human agents for customer service?
Customer preferences vary based on the type of inquiry and interaction complexity. Research indicates customers appreciate AI agents for routine questions that require quick, accurate responses and twenty-four-hour availability. Human agents remain preferred for complex problems, emotional situations, and issues requiring empathy or nuanced judgment.
Customer acceptance improves when AI agents clearly identify themselves, provide accurate information, and offer easy access to human assistance when needed. Organizations report higher satisfaction rates when AI agents acknowledge their limitations and proactively escalate appropriate issues to human staff.

