Artificial intelligence in human resources refers to software systems that automate, analyze, and optimize people management tasks across organizations.
HR departments face mounting pressure to do more with less while improving employee experiences and making better hiring decisions. Traditional manual processes struggle to keep pace with modern workforce demands. Many organizations spend countless hours on repetitive tasks like resume screening, scheduling interviews, and answering routine employee questions.
AI offers solutions to these challenges by handling routine work and providing data-driven insights. Machine learning algorithms can screen thousands of resumes in minutes, chatbots can answer employee questions instantly, and predictive analytics can identify which employees might leave before they do. These capabilities free HR professionals to focus on strategic work that requires human judgment.
The technology has moved beyond experimental phases into practical business applications. Research from the IBM Institute shows that 38 percent of organizations currently use AI for HR functions, with 62 percent planning implementation within three years.

Source: Lattice
What AI Means for Modern Human Resources
Artificial intelligence in human resources refers to computer systems that can perform tasks traditionally requiring human intelligence, such as screening resumes, answering employee questions, and analyzing workforce patterns. AI transforms HR departments from reactive administrative functions into proactive strategic partners.
Unlike traditional HR software that follows predetermined rules and workflows, AI systems learn from data to make decisions and improve their performance over time. Traditional HR automation might sort resumes based on specific keywords, while AI can understand context and evaluate candidates against successful employee profiles.
Machine learning represents the foundation of most HR AI applications. These systems analyze large amounts of historical data to identify patterns and make predictions about future outcomes. For example, machine learning algorithms can examine years of employee performance data, engagement surveys, and retention records to predict which employees might leave the company within the next six months.
Natural language processing enables AI systems to understand and generate human language in ways that feel natural and conversational. HR chatbots use natural language processing to answer employee questions about benefits, policies, and procedures in plain English rather than requiring employees to navigate complex menu systems.
How AI Transforms Core HR Functions
Artificial intelligence is reshaping human resources across every stage of the employee journey, from the moment someone applies for a job until they retire. AI systems now handle tasks that once required hours of human effort and provide insights that help organizations make better workforce decisions.
Recruitment and Talent Acquisition
AI-powered resume screening systems scan thousands of applications in minutes, identifying candidates whose skills and experience match job requirements. Machine learning algorithms analyze resume content, social media profiles, and professional networks to find qualified candidates who might not have applied directly.

Source: ResearchGate
Candidate matching algorithms compare applicant qualifications against job descriptions, ranking candidates based on predicted performance and cultural fit. T-Mobile's AI-optimized job descriptions attract 17 percent more women applicants and fill positions five days faster than traditional approaches.
Automated initial interviews use conversational AI to conduct preliminary candidate screenings. Video interview analysis examines facial expressions, speech patterns, and word choice to assess candidate responses, though this application faces increasing regulatory scrutiny due to bias concerns.
Employee Onboarding and Development
Personalized learning paths adapt training content based on individual employee roles, experience levels, and learning preferences. AI systems analyze how employees engage with training materials and adjust content delivery timing and format to optimize learning outcomes.
AI agents in customer service platforms provide real-time feedback and guidance to new employees as they navigate job responsibilities and organizational processes. Virtual assistants handle routine onboarding tasks such as account setup, document processing, and system access provisioning.
Skills gap analysis compares current employee capabilities against future organizational requirements, identifying areas where additional training or hiring is needed. Career pathing recommendations suggest development opportunities and potential advancement routes based on employee skills, interests, and organizational needs.
Performance Management and Analytics
Real-time feedback systems collect performance data continuously rather than relying on annual reviews. AI algorithms analyze productivity metrics, project outcomes, peer feedback, and customer interactions to provide comprehensive performance insights.
Sentiment analysis examines employee communications including emails, chat messages, and survey responses to gauge engagement levels and identify potential issues. Natural language processing identifies themes in employee feedback and flags concerns that require management attention.
Predictive performance modeling uses historical data to forecast future employee performance and identify factors that contribute to success or failure. Machine learning algorithms consider multiple variables including skills, experience, training participation, and team dynamics to predict performance outcomes.
Benefits of AI Implementation in HR
Organizations implementing artificial intelligence in human resources report measurable improvements across operational efficiency, cost reduction, and decision-making quality. These benefits translate into concrete return on investment metrics that justify AI technology adoption.
Operational Efficiency and Time Savings
AI automation reduces time spent on routine HR tasks by 60 to 70 percent, allowing HR professionals to focus on strategic activities. Organizations report significant acceleration in core HR processes through machine learning and automated workflows.

Source: HRD America
- Resume screening — 90 percent reduction in initial candidate review time
- Interview scheduling — 85 percent faster coordination between candidates and hiring teams
- Employee onboarding — 60 percent reduction in new hire setup and documentation processing
- Employee query resolution — Response time decreased from two days to 24 hours
RingCentral experienced a 40 percent increase in candidate pipeline volume while improving pipeline quality by 22 percent. These improvements compound across large organizations where thousands of HR transactions occur monthly.
Cost Reduction and ROI Metrics
AI implementation delivers measurable financial returns through reduced operational costs and improved workforce outcomes. Survey data from 600 HR leaders shows a median ROI of 15 percent, with top-performing organizations achieving returns exceeding 55 percent.
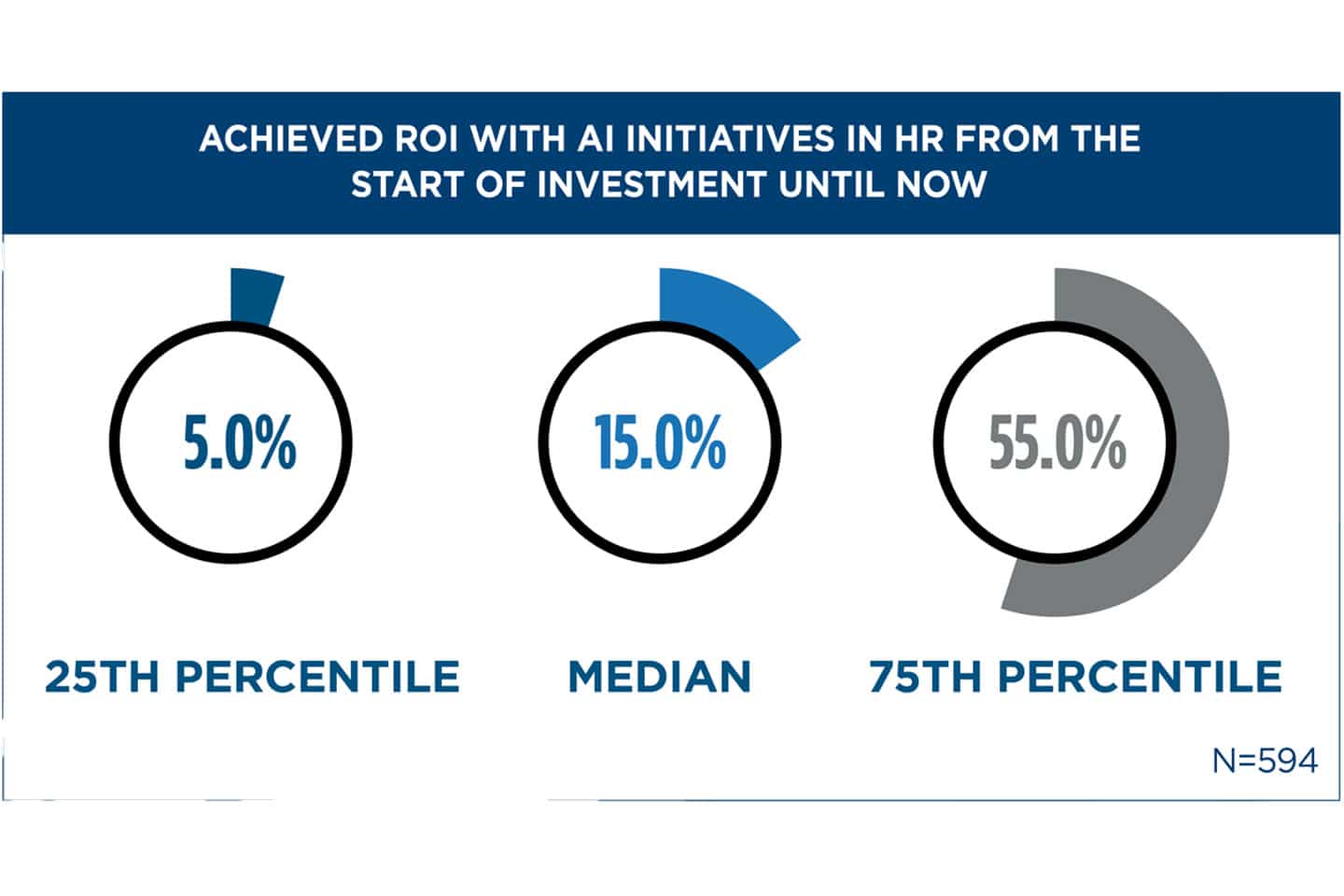
Source: HR Executive
Organizations report reduced turnover expenses through predictive analytics that identify at-risk employees before they resign. Early intervention programs powered by AI data analysis decrease voluntary turnover by 15 to 25 percent.
Training overhead decreases as AI systems personalize learning paths and automate administrative tasks. Manipal Health Enterprises saved over 60,000 employee hours annually through AI-powered virtual assistants.
Enhanced Decision Making Through Data
AI transforms HR decision-making from intuition-based approaches to evidence-driven strategies using comprehensive data analysis. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns in employee behavior, performance metrics, and organizational dynamics that human analysis cannot detect reliably.
Predictive models analyze historical performance data, engagement surveys, productivity metrics, and behavioral indicators to forecast employee outcomes. These systems predict turnover risk with 85 percent accuracy, allowing proactive retention interventions.
Unilever eliminated unconscious bias from early recruitment stages while reducing interview time by 70,000 hours annually. These systems evaluate candidates against objective criteria, reducing hiring bias and improving selection quality.
Strategic Considerations for Successful AI Adoption
Organizations face three critical areas when implementing AI in HR systems. Each area requires careful planning and ongoing management to ensure responsible AI deployment that protects both organizational interests and employee rights.
Data Privacy and Security Requirements
AI systems in HR process vast amounts of sensitive employee information including performance data, health records, salary details, and personal communications. The General Data Protection Regulation establishes strict requirements for processing personal data of EU residents, while state-level privacy laws in the United States create additional compliance obligations.
Data storage practices affect compliance and security outcomes. Organizations typically implement encryption for data both during transmission and while stored in databases. Access controls limit system access to authorized personnel based on job responsibilities and business requirements.
Employee consent requirements vary by jurisdiction and data type. GDPR requires clear legal bases for processing personal data, which may include legitimate business interests, contractual necessity, or explicit employee consent. Organizations maintain records of consent and provide mechanisms for employees to review, correct, or request deletion of their personal information.
Bias Prevention and Algorithmic Fairness
AI systems can perpetuate or amplify existing biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes in hiring, performance evaluation, and promotion decisions. The European Union's AI Act classifies HR-related AI systems as high-risk applications requiring specific bias mitigation measures.
Source: ResearchGate
Training data quality directly affects AI system fairness. Historical HR data often reflects past discriminatory practices or unequal representation across demographic groups. Organizations audit training datasets to identify potential bias sources and implement data cleansing processes to remove discriminatory patterns.
Regular bias audits evaluate AI system outcomes across protected characteristics including gender, race, age, and disability status. Testing protocols compare decision rates and outcomes between demographic groups to identify statistically significant disparities.
New York City's Local Law 144 requires annual bias audits for automated employment decision tools used within the city. Human oversight mechanisms provide safeguards against biased AI decisions through appeals processes and human review options.
Integration with Existing HR Technology
HR departments typically operate multiple technology platforms including applicant tracking systems, human resource information systems, payroll platforms, and performance management tools. AI implementation requires careful integration across these existing systems to achieve seamless data flow and user experiences.
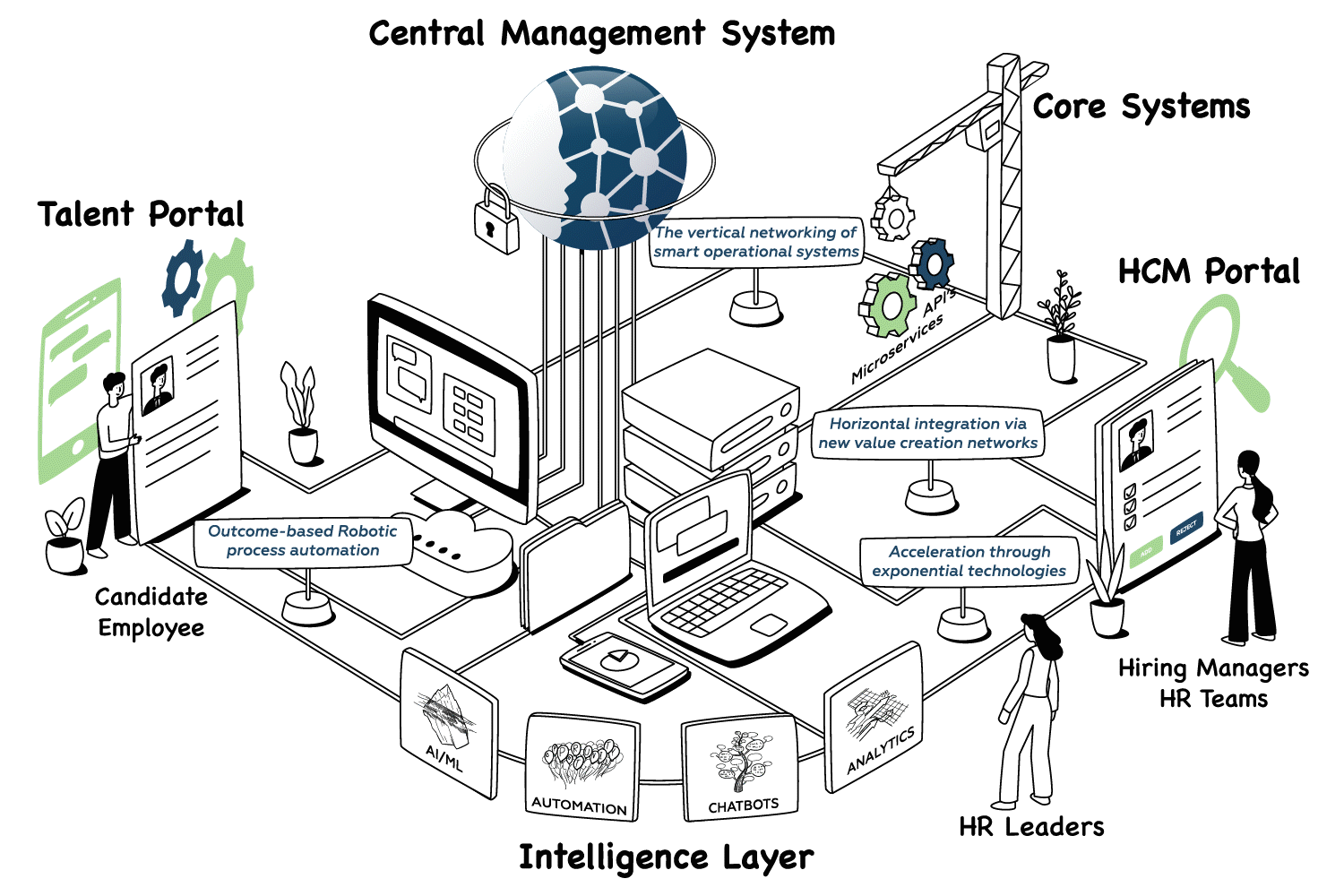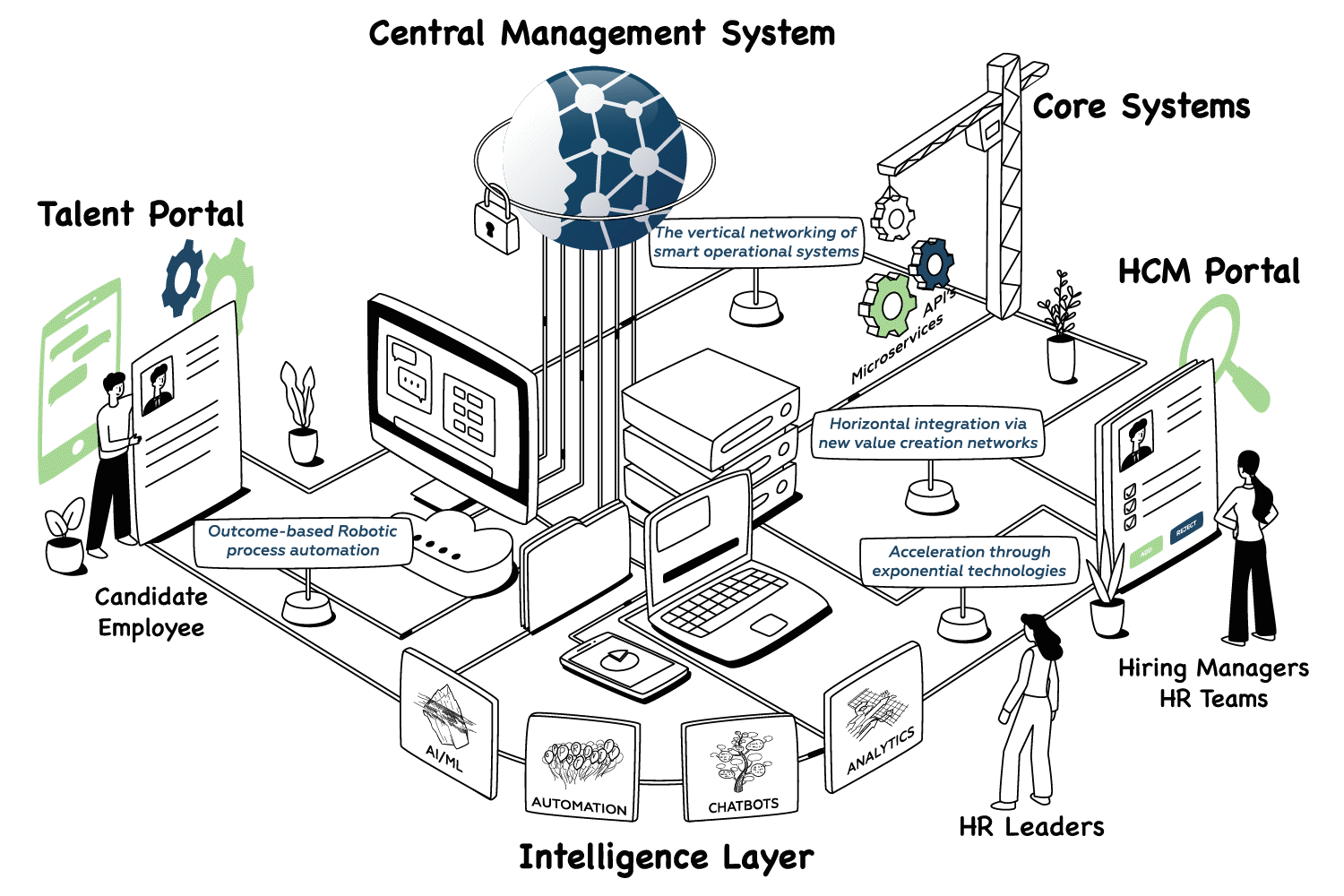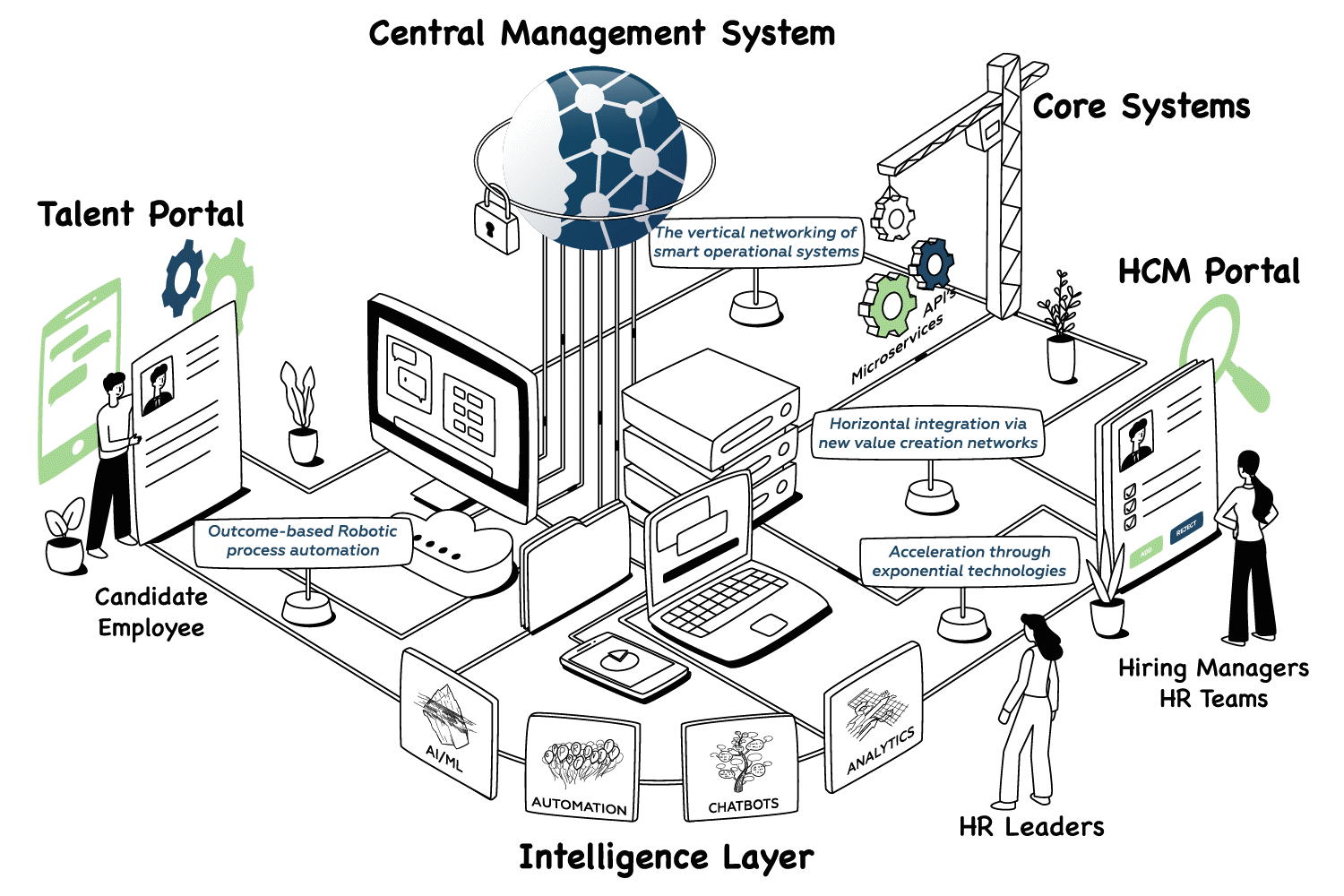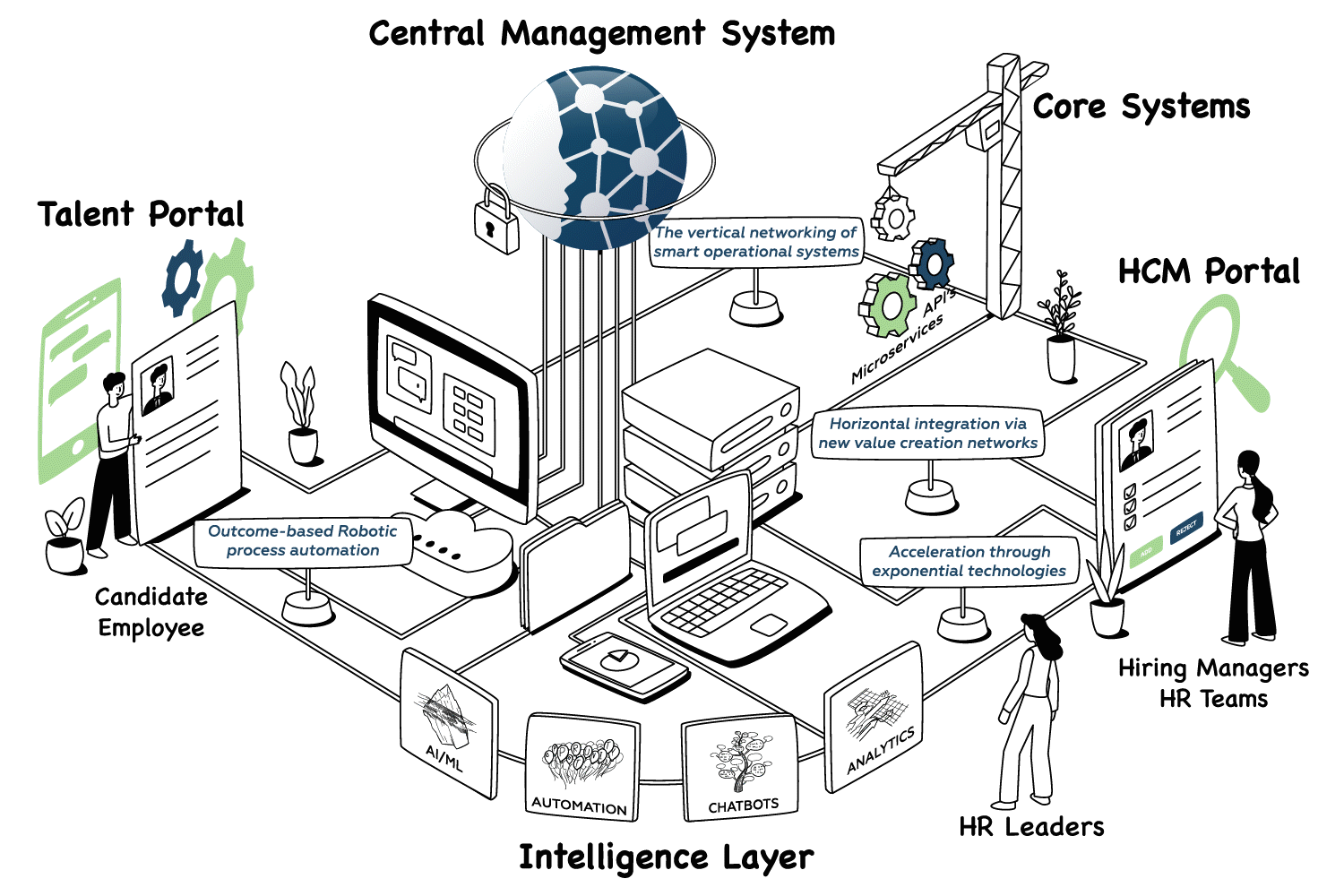
Source: EVA.ai
Application Programming Interface (API) compatibility determines how effectively AI systems connect with existing HR platforms. Organizations evaluate vendor API documentation and integration capabilities before selecting AI solutions.
Data migration presents technical and operational challenges during AI implementation. Employee records often exist in different formats across multiple systems with varying data quality standards. Migration projects include data mapping exercises to align information across systems and validation procedures to ensure accuracy after migration.
Change management strategies address employee adaptation to new AI-integrated workflows. AI change management training programs teach users how to navigate updated interfaces and leverage AI capabilities effectively. Communication plans explain system changes and provide ongoing support during transition periods.
Overcoming Common AI Implementation Challenges
Organizations face predictable obstacles when deploying AI systems for human resources functions. These challenges span people, technology, and skills dimensions, but each has proven solutions that reduce implementation risk and improve success rates.
Change Management and Employee Adoption
Employee resistance represents the most frequent barrier to successful AI implementation in HR. Workers often express concerns about job displacement, privacy invasion, and loss of human connection in workplace interactions.
Communication strategies address employee concerns through transparency and education. Organizations achieve better adoption outcomes when they maintain open dialogue about AI implementation objectives. Clear explanations of how AI systems work and what data they use help reduce anxiety about unknown processes.
Stakeholder buy-in techniques involve key influencers in the implementation process. Change champions from different departments and levels help spread positive messages about AI adoption. Executive sponsorship signals organizational commitment while providing resources and authority to overcome obstacles.
Phased rollout approaches reduce implementation risk while building confidence through early wins. Organizations typically begin with pilot programs targeting specific use cases before expanding to enterprise-wide deployment. These pilots allow teams to refine systems and develop best practices before broader implementation.
Technical Integration Solutions
Legacy systems create significant technical challenges for AI implementation since many HR departments operate older technology platforms that lack modern integration capabilities. Organizations must evaluate existing system architectures and plan integration strategies that maximize AI benefits.
Legacy system compatibility requires careful assessment of existing HR technology stacks. Many applicant tracking systems, payroll platforms, and employee databases use older data formats and limited API capabilities that complicate AI integration.
Cloud versus on-premise considerations affect cost, security, and scalability outcomes for AI implementations. Cloud platforms offer faster deployment, automatic updates, and reduced infrastructure management overhead. On-premise solutions provide greater control over data security and system customization but require significant internal technical expertise.
Vendor selection criteria guide organizations toward AI partners that support long-term success rather than short-term functionality. Key technical requirements include data security certifications, API compatibility with existing HR systems, bias testing procedures, and regulatory compliance capabilities.
Skills Development and Training Needs
AI implementation success depends heavily on workforce capabilities that span both technical and strategic competencies. Organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs that prepare HR professionals for AI-augmented work environments.
HR team upskilling addresses the evolving requirements of human resources professionals who must manage AI systems while maintaining strategic focus on human capital optimization. Technical literacy requirements include understanding AI system capabilities and limitations, interpreting AI-generated insights, and recognizing signs of algorithmic bias.
AI literacy programs build organizational understanding of artificial intelligence capabilities, applications, and implications. These programs typically include basic concepts of machine learning, specific applications of AI in HR contexts, ethical considerations, and practical skills for interacting with AI tools.
Ongoing education requirements reflect the rapidly evolving nature of AI technology and regulatory environments. Organizations must establish continuous learning cultures that keep pace with technological advancement and changing business requirements.
Compliance and Ethical AI in Human Resources
Organizations using artificial intelligence in HR face complex legal and ethical requirements that protect employees while enabling effective talent management. These frameworks establish boundaries for AI use in hiring, performance evaluation, and workplace monitoring. Responsible AI practices require ongoing attention to compliance requirements and ethical considerations.
Regulatory Framework Navigation
The European Union's AI Act, effective since August 2024, classifies HR AI systems as high-risk applications requiring extensive compliance measures. This regulation prohibits emotion recognition AI in workplace settings and mandates bias audits for recruitment and evaluation systems.
Employment law applies to AI systems the same way it applies to human decision-makers. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission treats algorithmic bias as a form of discrimination under existing civil rights laws, making organizations liable for biased AI outcomes.
Documentation requirements include maintaining records of AI system design decisions, training data sources, algorithm performance metrics, and audit results. Organizations must preserve decision logs that show how AI systems reached specific conclusions about individual employees or candidates.
International compliance creates additional complexity for multinational organizations. The EU AI Act requires registration of high-risk HR systems in European databases, while Asian markets are developing their own AI governance frameworks.
Protecting Employee Rights and Privacy
Transparency requirements mandate clear communication about AI use in employment decisions. Employees have the right to know when AI influences decisions affecting their work, including hiring, performance evaluation, promotion, and termination.
Employee notification procedures require advance warning before implementing new AI systems that affect working conditions. Some jurisdictions mandate consultation with employee representatives or unions before deploying AI tools for workforce management.
Data subject rights under privacy laws include access to personal data used in AI systems, correction of inaccurate information, and deletion of data in certain circumstances. Appeals processes provide mechanisms for challenging AI decisions through human review and alternative assessment methods.
FAQs About AI in Human Resources
How long does it take to implement AI in HR recruitment systems?
Implementation timelines for AI recruitment tools typically range from three to six months. Simple applications like resume screening or candidate matching often deploy within three months for organizations with clean data and modern HR systems. More complex implementations involving multiple recruitment platforms or custom integrations may require six months or longer.
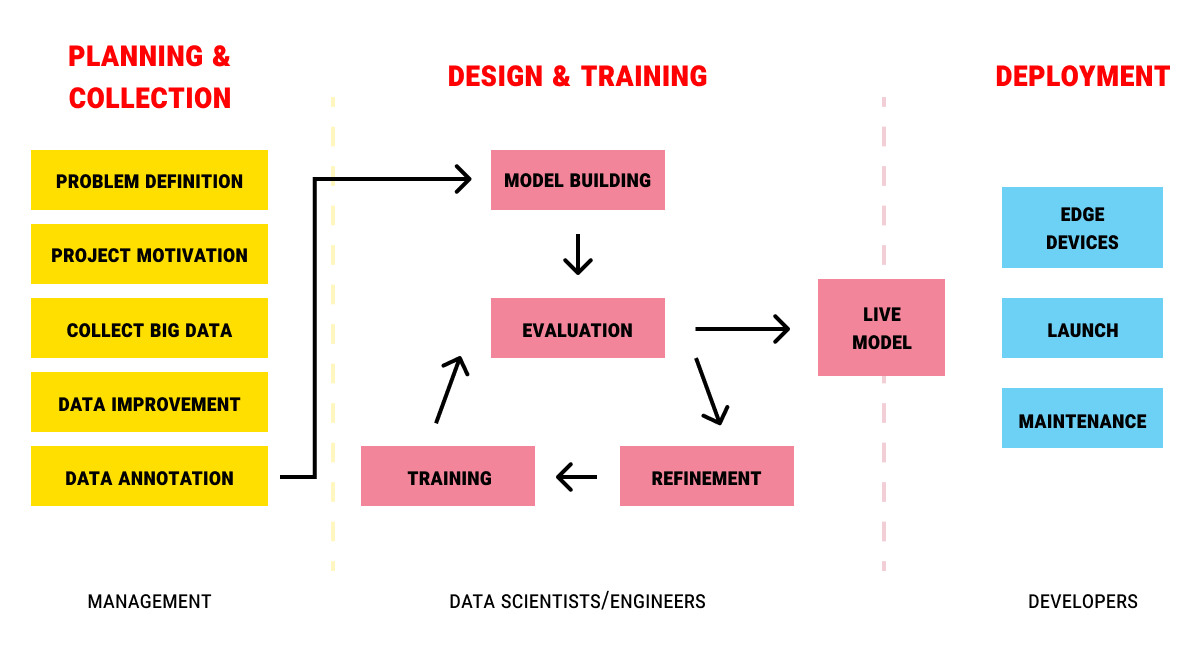
Source: Label Your Data
Organizations with legacy systems or poor data quality require additional time for data preparation and system integration before AI deployment can begin. Cloud-based solutions generally implement faster than on-premise alternatives.
What specific costs should companies expect when implementing HR AI systems?
Initial investments for HR AI systems range from $50,000 annually for small business cloud solutions to several million dollars for enterprise implementations with custom development. Organizations typically allocate 60 to 70 percent of budgets to software licensing and implementation, 20 to 30 percent to training and change management, and 10 to 15 percent to ongoing maintenance.
Ongoing operational costs include subscription fees, system maintenance, training updates, and compliance auditing. Research shows organizations achieve median return on investment of 15 percent, with leading implementations exceeding 55 percent through operational efficiency gains.
How do companies prevent AI bias in employee performance evaluations?
Organizations prevent bias in AI performance systems through diverse training data that represents all employee demographics, regular bias audits that test outcomes across protected characteristics, and continuous monitoring systems that track AI decisions in real-time to detect discriminatory patterns.
Technical approaches include adversarial debiasing, which trains AI systems to make decisions without relying on protected attributes, and fairness-aware algorithms that incorporate equity constraints. Human oversight mechanisms provide additional safeguards through diverse review teams and appeals processes.
Which HR functions benefit most from AI automation?
Resume screening and candidate matching show the highest impact from AI automation, with organizations reporting 90 percent reductions in initial review time and 17 percent improvements in candidate quality. Employee onboarding processes achieve 60 percent time reductions through automated documentation and system provisioning.
Performance management benefits significantly from AI-powered analytics that provide continuous feedback rather than annual reviews. Predictive analytics for employee retention achieve 85 percent accuracy in identifying at-risk employees, enabling proactive intervention strategies.
What regulatory compliance requirements apply to AI in HR?
The EU AI Act classifies HR AI systems as high-risk applications requiring bias audits, transparency documentation, and human oversight mechanisms. New York City's Local Law 144 mandates annual bias audits for automated employment decision tools and requires public disclosure of audit results.
GDPR establishes data protection requirements for AI systems processing employee personal information, including consent management, data subject rights, and cross-border transfer restrictions. Organizations must maintain compliance documentation and provide employee access to AI decision-making processes.

