ISO 42001 is an international standard that provides a framework for organizations to manage artificial intelligence systems responsibly and systematically.
Published in December 2023, ISO 42001 represents the first global standard specifically designed for artificial intelligence management systems. The standard addresses growing concerns about AI safety, transparency, and ethical deployment across industries. Organizations worldwide face increasing pressure to demonstrate responsible AI practices to customers, regulators, and stakeholders.
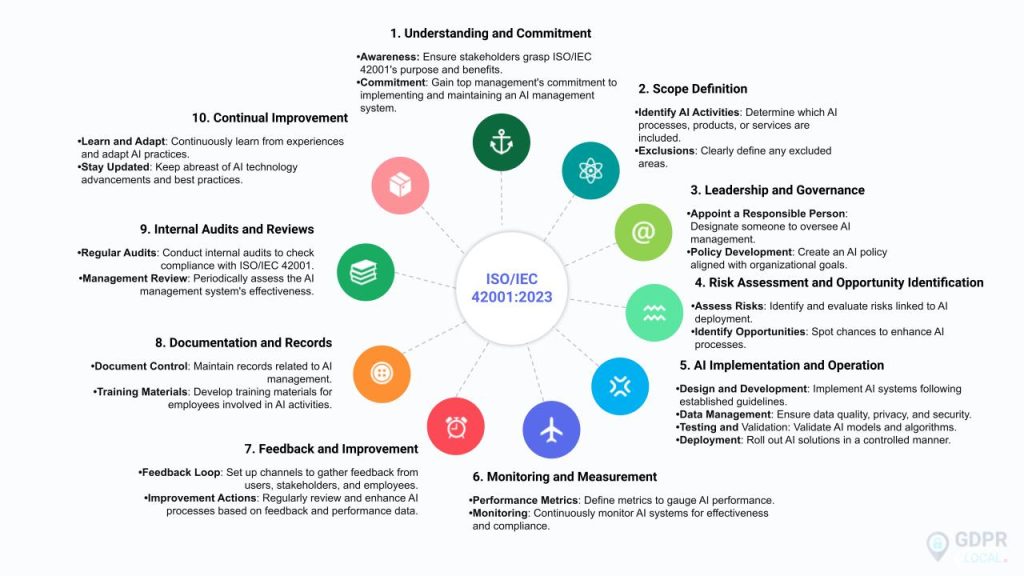
ISO 42001 framework structure and components. Source: GDPR Local
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) developed ISO 42001 to fill a critical gap in AI governance. Traditional IT management standards proved insufficient for addressing the unique challenges of artificial intelligence systems. AI systems can learn, adapt, and make decisions in ways that require specialized oversight and control mechanisms.
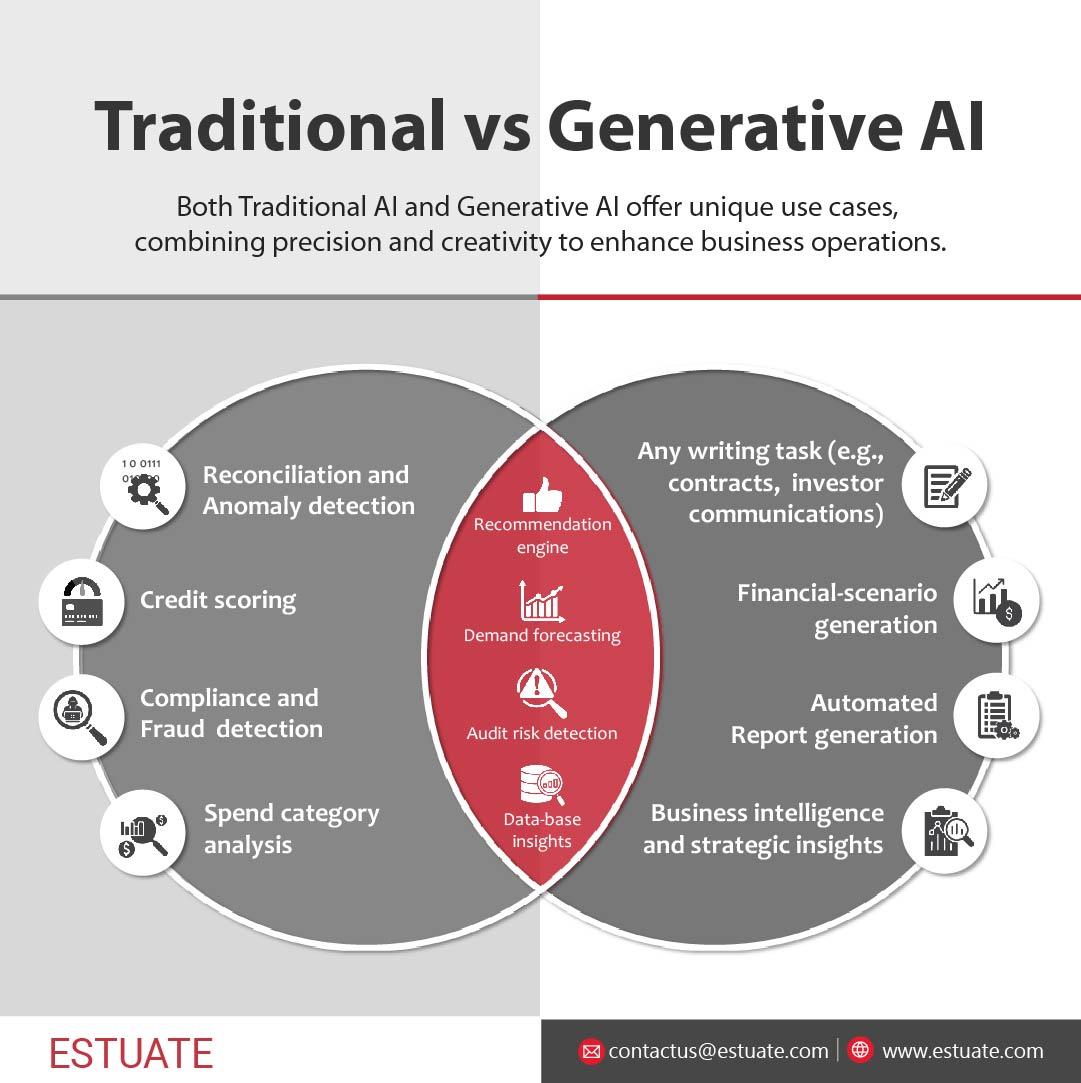
Comparison of traditional AI and generative AI challenges. Source: Estuate
What Is ISO 42001
ISO/IEC 42001:2023 is the world’s first international standard specifically designed for artificial intelligence management systems (AIMS). The standard provides organizations with a comprehensive framework for establishing, implementing, and maintaining responsible AI governance throughout the complete lifecycle of AI systems.
Unlike voluntary guidelines or recommendations, ISO 42001 establishes auditable requirements that organizations can implement and achieve certification against. The standard creates measurable and verifiable approaches to AI governance that external auditors can assess.
The scope of ISO 42001 applies to organizations of all sizes across all industries that develop, provide, or use AI-based products or services. This includes technology companies creating AI solutions, businesses implementing AI to improve operations, government agencies using AI for citizen services, and healthcare organizations deploying AI for patient care.
The standard addresses AI-specific challenges that traditional IT management standards cannot adequately handle. These challenges include algorithmic bias, lack of transparency in AI decision-making, data privacy concerns, and unpredictable system behaviors that can emerge as AI systems learn and adapt over time.
Core Requirements of ISO 42001

ISO 42001 ten clauses organizational structure. Source: ISO Templates & Documents
ISO 42001 establishes ten main clauses for artificial intelligence management systems, with clauses 4-10 containing the auditable requirements organizations must satisfy for certification. The standard follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act model used in other ISO management standards, creating a structured approach to AI governance.
Organizations implementing ISO 42001 must define their scope clearly, identifying which AI systems, processes, and functions fall within their AI management system boundaries. Leadership commitment requires top management to demonstrate active support through resource allocation, policy establishment, and regular performance reviews.
Risk Assessment and Management

Risk assessment matrix for AI systems showing categorization and prioritization. Source: AWS
Organizations conduct comprehensive risk assessments that address AI-specific challenges throughout the system lifecycle. The risk management process identifies technical risks such as system failures and security vulnerabilities, ethical risks including bias and discrimination, and regulatory risks related to emerging AI compliance requirements.
Risk assessment methodologies account for unique AI characteristics including systems that learn and adapt over time, dependence on training data quality, and potential impacts on individuals and society. Organizations evaluate both intended and unintended consequences of AI system deployment.
Key risk management components include:
- Risk identification processes — Address algorithmic bias, model drift, adversarial attacks, and unintended AI behaviors
- Impact assessment procedures — Evaluate consequences on individuals, organizations, and society
- Risk treatment strategies — Include avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance with monitoring
- Documentation requirements — Provide evidence for risk decisions and implementation
- Regular risk review cycles — Address evolving AI technologies and changing threat landscapes
AI System Lifecycle Controls
AI system lifecycle phases with control points. Source: ResearchGate
ISO 42001 requires systematic controls across all phases of AI system development, deployment, and operation. Organizations establish procedures that incorporate appropriate safeguards from initial design through eventual system retirement.
Development phase controls ensure AI systems include proper testing procedures, validation mechanisms, and safety features. Organizations implement technical specifications for data quality, model training, and performance validation before systems enter production environments.
Deployment controls address safe introduction of AI systems into operational settings, including procedures for monitoring system performance and detecting unusual behaviors. Post-deployment controls focus on ongoing system maintenance, performance monitoring, and adaptation management.
Documentation and Monitoring
Organizations maintain comprehensive documentation covering AI management system policies, procedures, risk assessments, and performance metrics. Documentation requirements extend beyond technical specifications to include governance decisions, stakeholder communications, and compliance evidence.
Monitoring systems track AI performance indicators, risk management effectiveness, and compliance with established policies. Organizations establish key performance indicators that provide meaningful insights into both technical system performance and governance effectiveness.
Benefits of ISO 42001 Certification
Organizations that implement ISO 42001 gain significant advantages in managing artificial intelligence systems responsibly. The international standard provides a structured framework that helps companies address AI-specific challenges while demonstrating their commitment to ethical AI practices.
Risk Mitigation and Compliance
ISO 42001 helps organizations identify and address AI-related risks before they become serious problems. The standard requires companies to develop systematic approaches for managing risks throughout the AI system lifecycle, from initial development through deployment and ongoing operation.
The framework addresses AI-specific challenges like algorithmic bias, model drift, and unpredictable system behaviors that traditional IT risk management approaches often miss. Organizations implement comprehensive risk assessment methodologies that account for the unique characteristics of AI systems.
Regulatory compliance becomes more manageable through ISO 42001 implementation. As governments worldwide introduce AI regulations like the EU’s AI Act, organizations with established AI governance frameworks can adapt more quickly to new requirements.
Competitive Advantage
ISO 42001 certification creates market differentiation opportunities for organizations competing in environments where AI governance matters. Companies can leverage their certification status to distinguish themselves from competitors who lack verified AI governance practices.
Early adopters report competitive advantages in sales processes, particularly when selling to customers who prioritize responsible AI practices. The third-party validation aspect of certification provides credible evidence that organizations take AI governance seriously.
Market access benefits emerge as certain industries and government contracts increasingly require evidence of AI governance capabilities. Organizations with ISO 42001 certification can access opportunities that may be unavailable to uncertified competitors, particularly in regulated sectors like healthcare and retail.
ISO 42001 vs Other AI Governance Frameworks
Understanding how ISO 42001 relates to other AI governance frameworks helps organizations choose the right approach for their needs. Each framework serves different purposes and offers distinct advantages depending on organizational goals and requirements.
ISO 42001 vs NIST AI Risk Management Framework

Comparison table highlighting key differences between ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF. Source: Trustible
ISO 42001 and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework represent two complementary approaches to AI governance that organizations often implement together. The NIST AI RMF provides detailed guidance on risk management practices, while ISO 42001 offers a certifiable management system standard.
The NIST AI RMF organizes AI governance around four core functions: Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage. The Govern function establishes organizational culture and structures for responsible AI development. Map focuses on understanding AI system context and potential impacts.
ISO 42001 takes a management system approach that integrates AI governance into organizational processes. The standard requires systematic implementation of policies, procedures, and controls throughout the AI lifecycle. Organizations can achieve third-party certification to validate their AI management system effectiveness.
Key structural differences distinguish these frameworks. NIST AI RMF remains voluntary and provides guidance for self-assessment and internal improvement. ISO 42001 establishes auditable requirements that certification bodies can assess, providing independent verification of AI governance practices.
ISO 42001 vs ISO 27001
ISO 42001 and ISO 27001 address different but related aspects of technology governance within organizations. Understanding their distinct purposes helps organizations determine appropriate implementation strategies and integration opportunities.
ISO 27001 establishes requirements for information security management systems, focusing on protecting information assets from security threats. The standard addresses confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information through systematic security controls and risk management processes.
ISO 42001 specifically addresses artificial intelligence management systems, focusing on responsible AI development, deployment, and operation. The standard emphasizes transparency, accountability, explainability, and fairness in AI systems.
Both standards share common management system principles, including leadership commitment, risk assessment, documentation requirements, and continuous improvement. Organizations with existing ISO 27001 implementations can leverage their management system experience when implementing ISO 42001.
How to Implement ISO 42001
Implementation timeline showing typical project phases and durations. Source: ISO Templates & Documents
Assessment and Planning
Organizations starting ISO 42001 implementation begin with comprehensive assessment of existing AI governance capabilities and current state analysis. This foundation enables informed planning decisions and realistic timeline development.
The assessment phase includes conducting gap analysis comparing current AI governance practices against ISO 42001 requirements across all ten clauses. Organizations inventory all AI systems, applications, and tools currently in use or development, including their purposes, risk levels, and stakeholder impacts.
Organizations assess organizational context by identifying internal factors like company culture, resources, and technical capabilities alongside external factors such as regulatory requirements and industry expectations. The process includes mapping stakeholder relationships and documenting all parties affected by or interested in AI systems.
System Design and Documentation
The documentation phase transforms assessment findings into formal management system components that meet ISO 42001 requirements. Organizations develop policies, procedures, and control frameworks that address AI-specific governance needs.
Organizations develop AI governance policy creating high-level policy statements articulating organizational commitment to responsible AI use, ethical principles, and compliance objectives. They design risk management processes establishing systematic procedures for identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and treating AI-related risks.
The documentation process includes creating impact assessment procedures, documenting lifecycle management procedures, and establishing data governance frameworks. Organizations design incident response procedures and create performance measurement frameworks with key performance indicators.
Training and Implementation
Training programs ensure personnel understand their roles in AI governance and possess necessary competencies for effective AIMS operation. Organizations develop comprehensive programs addressing different audiences and skill requirements.
Organizations assess competency requirements identifying specific knowledge, skills, and experience requirements for different roles involved in AI system development, deployment, and oversight. They design role-specific training curricula creating targeted training programs for technical staff, managers, executives, and other personnel.
The training process includes developing AI ethics training modules addressing ethical considerations, bias recognition, fairness principles, and responsible AI practices. Organizations implement technical skills development providing training on AI risk assessment methodologies, monitoring tools, and incident response procedures.
ISO 42001 Certification Process
Organizations pursue ISO 42001 certification through accredited certification bodies that evaluate their artificial intelligence management systems. The certification process follows established procedures for management system standards, providing independent validation that an organization meets ISO 42001 requirements.
Certification Requirements
Organizations complete several preparation activities before pursuing formal certification. The preparation phase typically requires six to twelve months, depending on existing AI governance maturity, available resources, and AIMS scope complexity.
Gap analysis against ISO 42001 requirements forms the foundation of preparation. Organizations evaluate their current AI governance practices against the standard’s requirements to identify areas requiring development or improvement.
Policy and procedure development addresses identified gaps. Organizations create or update documentation covering AI governance policies, risk assessment procedures, impact assessment methodologies, and operational controls.
Audit Process and Timeline
The certification audit process consists of two primary stages following ISO/IEC 17021-1 procedures. The timeline spans several months from initial application to certificate issuance, with specific durations varying based on organizational complexity and AIMS scope.
Stage 1 audits assess organizational readiness for full certification evaluation. Auditors review AIMS design, documentation, and policy frameworks during this preliminary assessment. Stage 1 audits typically require one to two days.
Stage 2 audits provide comprehensive evaluation of AIMS implementation and operational effectiveness. Auditors conduct detailed interviews with personnel, observe operational processes, and examine evidence of AIMS performance and continuous improvement. Stage 2 audit duration varies from one to three weeks based on organizational size and complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions About ISO 42001
What organizations can get ISO 42001 certified?
ISO 42001 applies to organizations of all sizes that develop or use AI systems. The standard’s flexibility allows organizations to define their scope based on their specific circumstances, resources, and AI portfolio. Small businesses can focus certification on their core AI systems while larger organizations may include comprehensive AI ecosystems.
How long does ISO 42001 implementation take?
Implementation timelines depend on the organization’s current AI governance maturity and the scope of AI systems included in the management system. Organizations typically require six to twelve months to prepare for certification audits. Organizations with existing management systems like ISO 27001 may implement faster by leveraging established processes.
Is ISO 42001 required by law?
ISO 42001 remains a voluntary standard, though regulatory requirements may make certification necessary for certain industries or markets. The European Union’s AI Act and other emerging regulations create compliance obligations that ISO 42001 can help address. Organizations in regulated sectors like healthcare and financial services may find certification becomes practically required to meet customer expectations.
How does ISO 42001 address algorithmic bias?
ISO 42001 includes requirements for bias assessment and mitigation as part of comprehensive AI risk management processes. Organizations must identify potential sources of bias in training data, algorithms, and decision-making processes during system development and ongoing operation. The standard requires systematic evaluation of AI system outputs for discriminatory patterns and implementation of controls to prevent or reduce biased outcomes.


