The AI arms race refers to the intense competition between major technology companies to develop the most advanced artificial intelligence systems and capture market dominance in this transformative technology sector.
Three companies have emerged as the primary competitors in this high-stakes battle. OpenAI leads with its ChatGPT platform and consumer-focused strategy. Google leverages decades of AI research and massive infrastructure advantages. Meta pursues an open-source approach while building AI into its social media empire.

Source: People Matters
The competition extends far beyond product development. Companies are investing hundreds of billions in specialized computing infrastructure, engaging in unprecedented talent wars with compensation packages exceeding $200 million, and racing to solve fundamental challenges in AI safety and capability.
Understanding the Core AI Competition
The AI arms race centers on three distinct approaches to artificial intelligence development. Each company brings different strengths that create unique competitive advantages.
OpenAI’s consumer-first strategy focuses on making AI accessible through simple interfaces like ChatGPT. The company reached approximately 800 million weekly users by October 2025 and hit its first $1 billion revenue month in July 2025.

Source: Demand Sage
Google’s integrated ecosystem leverages existing products like Search, Gmail, and Android to distribute AI capabilities. The company controls custom hardware through Tensor Processing Units and maintains decades of AI research experience.
Meta’s open-source approach releases Llama models freely while building AI into Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp. This strategy has generated more than 650 million downloads of Llama models by late 2024.
How Platform Capabilities Actually Compare
The three platforms excel in different areas based on their design priorities and business models.
Technical Performance Differences
OpenAI’s latest models show approximately 45 percent fewer factual errors compared to previous generations. The platform emphasizes conversational AI and reasoning capabilities for general consumer use.
Google’s Gemini integrates with existing Google services and demonstrates strong performance in mathematical reasoning tasks. The platform achieved gold-medal performance at mathematical competitions through its Deep Think model.
Meta’s Llama 4 supports 200 languages with over 100 languages having more than one billion training tokens each. The open-source nature allows developers to customize models for specific applications.
Business Model and Pricing Structures
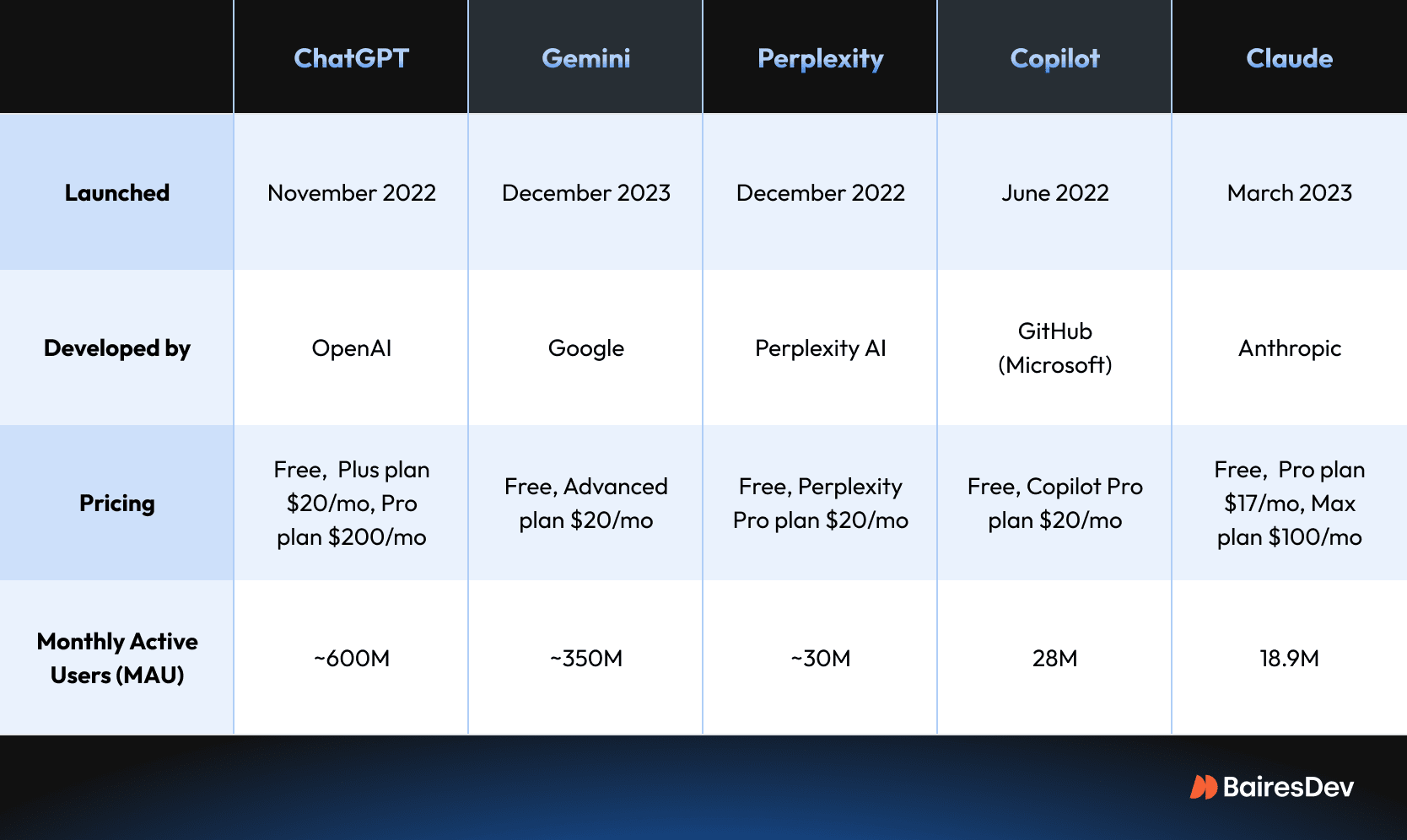
Source: BairesDev
- OpenAI — Usage-based pricing with ChatGPT Plus at $20 monthly and Enterprise at $60 per user monthly
- Google — Gemini Enterprise at $30 per user monthly, reduced to $14 when bundled with Workspace
- Meta — Open-source models available without licensing fees, though organizations pay for computing infrastructure
Enterprise Features and Integration
Google offers pre-built integrations with Salesforce, SAP, and other business applications through existing Workspace administrative tools. Organizations can implement Gemini without specialized AI engineering skills.
OpenAI requires custom integration work through APIs and developer tools. Companies develop applications using OpenAI’s frameworks but assume technical implementation responsibilities. For organizations considering these integrations, conducting an AI maturity assessment helps evaluate readiness for implementation.
Meta’s approach demands the highest technical expertise including model deployment, infrastructure management, and ongoing optimization. Organizations either develop internal AI capabilities or partner with AI consulting services for specialized implementation support.
Infrastructure Investment Driving Competition
AI companies are building massive computing infrastructure to train and operate their AI systems. The United States added 5.8 gigawatts of data center capacity in 2024 alone, compared to 1.6 gigawatts in the European Union.

Source: Synergy Research Group
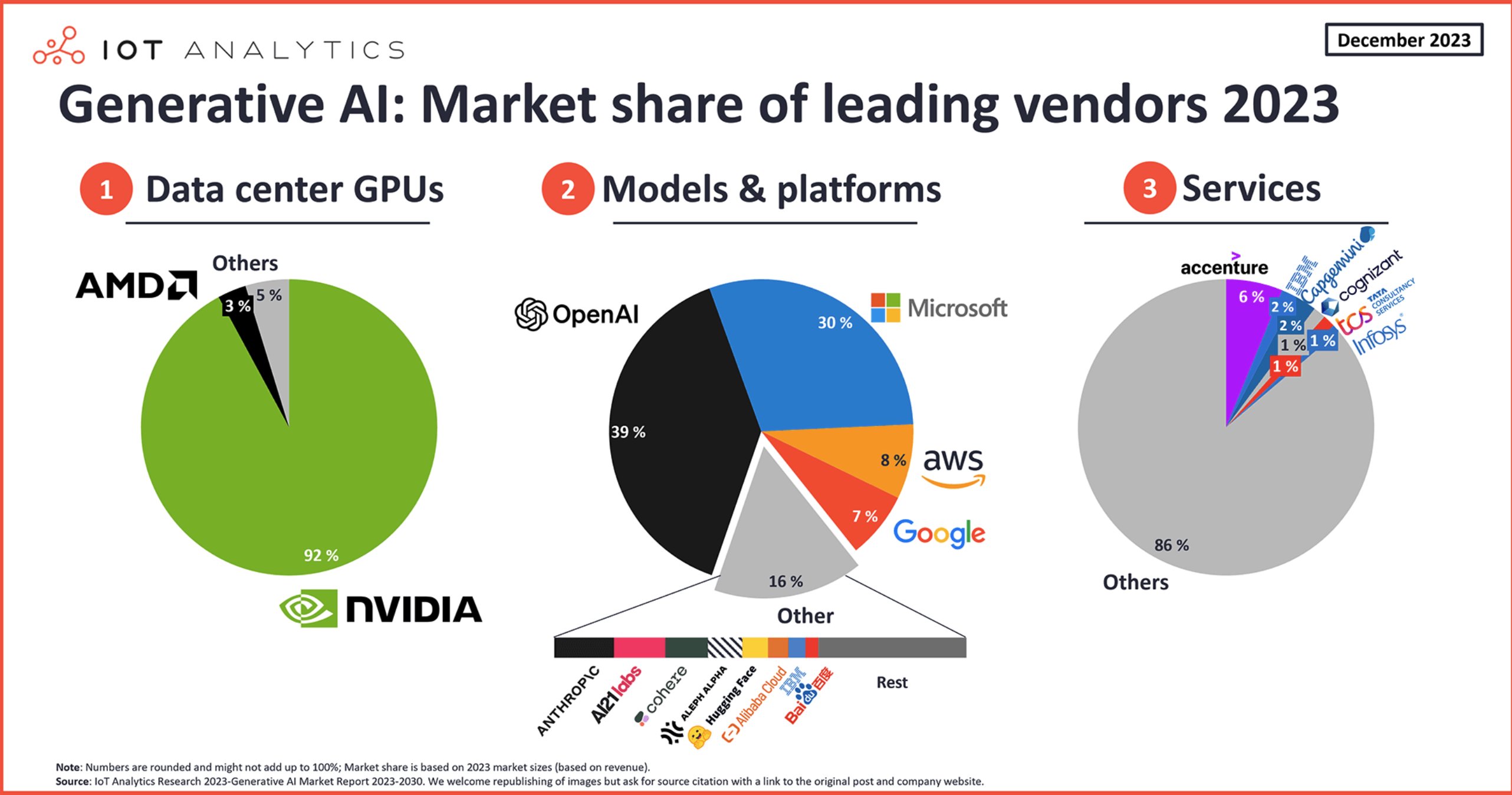
Most companies rely on graphics processing units manufactured by NVIDIA, which controls 92 percent of the data center GPU market worth $125 billion in 2024. This dependency creates strategic risks as companies compete for limited supplies.
Source: X
Google has developed custom Tensor Processing Units to reduce reliance on NVIDIA hardware. These specialized chips provide cost advantages and performance improvements tailored to Google’s specific AI applications.
The Talent War Reshaping AI Development
Competition for AI researchers has reached unprecedented levels. Elite researchers now command compensation packages that sometimes exceed $200 million, with Meta reportedly offering select researchers up to $1 billion over multiple years.

Source: Menlo Ventures
The talent shortage stems from basic supply and demand. Fewer than 40,000 computer researchers work across all sectors in the United States, representing a tiny fraction compared to more than 1.6 million software developers.
Major companies recruit entire research teams to preserve collaborative relationships. Meta recently recruited at least eight to ten senior researchers from OpenAI, targeting people who had worked together on advanced reasoning projects.
Strategic Considerations for Organizations
Companies evaluating AI platforms face several key decisions that affect long-term technology strategy.

Source: ResearchGate
Platform Selection Criteria
Technical requirements vary significantly across vendors. Organizations evaluate model capabilities against specific use cases like customer service automation, content generation, or data analysis. Companies exploring AI for call centers often find different platforms excel at different aspects of customer service.
Integration complexity differs based on existing business systems. Google’s platform works directly with Workspace and common business applications, while OpenAI requires custom development work.
Vendor stability includes financial health and strategic commitments. Google’s established infrastructure provides stable foundations, while OpenAI’s rapid growth creates questions about long-term sustainability despite strong revenue growth.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-in
Organizations can prevent dependency on single providers through multi-platform strategies. This approach involves using standardized APIs, maintaining data in portable formats, and building systems that work with different AI models.
Contracts should include data portability clauses and avoid proprietary formats that only work with one vendor. Teams benefit from maintaining expertise across multiple platforms rather than specializing in one system.
Hybrid Implementation Approaches
Hybrid strategies use different providers for different tasks based on their strengths. One platform might excel at language processing while another performs better for image analysis or data processing.
This approach requires coordination between platforms but provides flexibility and performance optimization. Companies can route different types of work to the most suitable AI system while maintaining redundancy for critical operations. Organizations implementing AI agents in sales often benefit from this hybrid approach to maximize effectiveness across different sales functions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which AI platform works best for companies with existing Google Workspace subscriptions?
Google’s Gemini Enterprise integrates directly with Workspace tools at $14 per user monthly when bundled with existing subscriptions. The platform provides AI capabilities through familiar interfaces without requiring separate applications or extensive training.
How do open-source AI models like Meta’s Llama compare to commercial options?
Meta’s Llama models eliminate licensing fees but require organizations to provide their own computing infrastructure and technical expertise. Companies with strong technical teams often find this approach more cost-effective for high-volume usage, while organizations preferring managed services typically choose commercial options.
What happens if an AI vendor changes their pricing or service terms?
Organizations can protect themselves by maintaining data backups, documenting integration processes, and establishing relationships with multiple vendors. Service agreements should include data export provisions and reasonable notice periods for service changes.
How much technical expertise do companies need to implement different AI platforms?
Google’s Gemini requires minimal technical expertise due to pre-built integrations with common business applications. OpenAI demands API development skills and custom integration work. Meta’s open-source models require the most technical expertise including infrastructure management and model optimization. Small businesses often benefit from starting with platforms requiring less technical complexity.
The AI arms race between OpenAI, Google, and Meta represents more than corporate competition — it’s shaping the technological foundation for the next decade. Each company offers distinct advantages: OpenAI’s consumer innovation, Google’s integrated ecosystem, and Meta’s open-source flexibility. Organizations benefit from understanding these differences to make informed decisions about AI platform adoption and avoid the risks of vendor dependence in this rapidly evolving landscape.